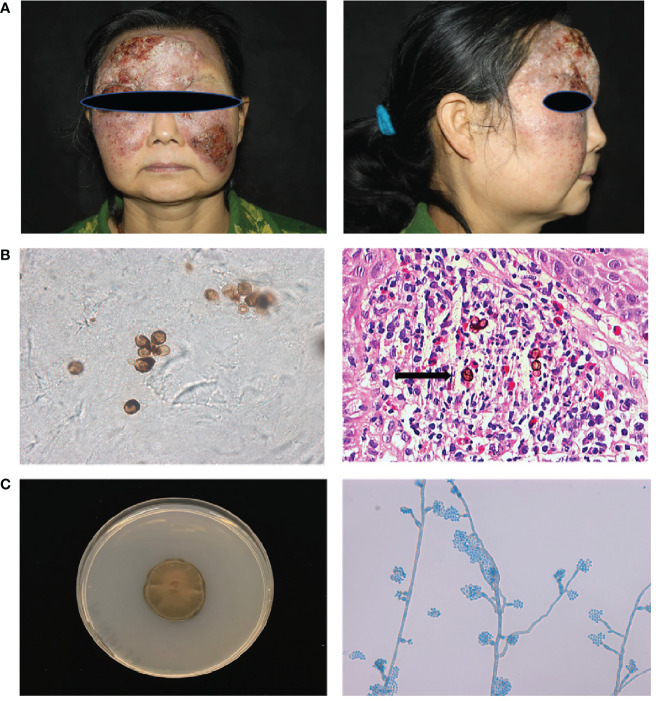
Figure 1.
Clinical features, laboratory findings of patient 1. (A) A protuberant dark red mass on the face with erosion, crust, and pus, which covered the forehead and cheek with a clear boundary. (B) Smear of the lesion scrapings showed brown sclerotic cells with cross septa. Histopathological examination of the skin lesion showed pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia of the epidermis, and intense dermal inflammatory infiltrations with the presence of sclerotic cells in the dermis (Haematoxylin and eosin stain; 400× original magnification) (C) Macroscopic appearance of the cultured pathogen: the colony was brown to blackish‐green with abundant short, grey aerial hyphae (Potato dextrose agar, 14 d at 28°C). Microscopic examination of the cultured organisms revealed vase-shaped sporogenous cells with collar-like structure and flower-like arrangement of small conidia.