Table 2.
Catalysis of NPOPs and Ag@NPOPs for the carboxylation of phenylacetylene with CO2 a.
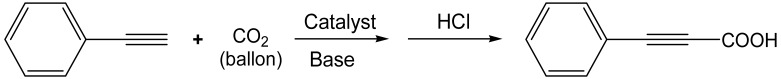
| |||||||
| Entry | Catalyst | Solvent | T/°C | Base (Amount/mmol) | Time /h |
Yield/% | TOF /h−1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Ag@NPOP-2 | DMSO | 60 | Cs2CO3(0.6) | 12 | 92.1 | 64.2 |
| 2 | Ag@NPOP-1 | DMSO | 60 | Cs2CO3(0.6) | 12 | 94.0 | 90.9 |
| 3 | NPOP-2 | DMSO | 60 | Cs2CO3(0.6) | 12 | 51.2 | |
| 4 | NPOP-1 | DMSO | 60 | Cs2CO3(0.6) | 12 | 55.4 | |
| 5 | Ag@NPOP-1 b | DMSO | 60 | Cs2CO3(0.6) | 12 | 94.2 | 36.4 |
| 6 | Ag@NPOP-1 | DMF | 60 | Cs2CO3(0.6) | 12 | 73.7 | 71.2 |
| 7 | Ag@NPOP-1 | ACN | 60 | Cs2CO3(0.6) | 12 | 11.9 | 11.5 |
| 8 | Ag@NPOP-1 | EtOH | 60 | Cs2CO3(0.6) | 12 | 3.4 | 3.3 |
| 9 | Ag@NPOP-1 | DMSO | 60 | K2CO3(0.6) | 12 | 11.5 | 11.1 |
| 10 | Ag@NPOP-1 | DMSO | 60 | DBU(0.6) | 12 | 51.0 | 49.3 |
| 11 | Ag@NPOP-1 | DMSO | 60 | NaOH (0.6) | 12 | 4.3 | 4.2 |
| 12 | Ag@NPOP-1 | DMSO | 60 | Cs2CO3(0.4) | 12 | 60.8 | 58.8 |
| 13 | Ag@NPOP-1 | DMSO | 60 | Cs2CO3(0.2) | 12 | 24.5 | 23.7 |
| 14 | Ag@NPOP-1 | DMSO | 50 | Cs2CO3(0.6) | 12 | 65.2 | 63.0 |
| 15 | Ag@NPOP-1 | DMSO | 40 | Cs2CO3(0.6) | 12 | 18.0 | 17.4 |
Reaction conditions: (a) Phenylacetylene (0.2 mmol), catalyst (2.0 mg), CO2 (balloon), solvent (1.0 mL). The reaction mixture was stirred at 60 °C for 12 h. Yield was calculated by 1H NMR. (b): catalyst, 5.0 mg.
