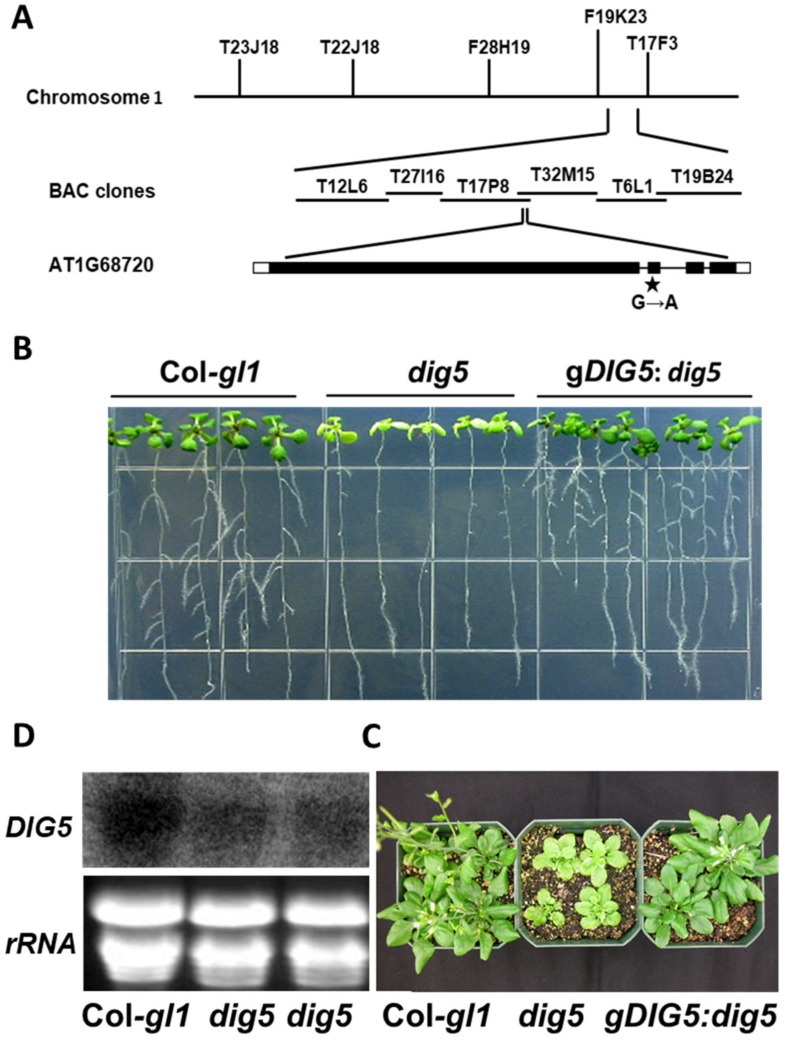
Figure 6.
Map-based cloning of the DIG5 locus and complementation of the dig5 mutants. (A) Map-based cloning of the DIG5 locus. After delimiting the DIG5 locus to an interval of about 105 kb, DNA sequencing identified a single nucleotide mutation in the gene At1g68720. (B,C) Complementation of the dig5 mutants with the wild type genomic DNA of At1g68720. Shown are the wild type Col-gl1, dig5, and dig5 mutant transformed with the wild type DIG5 genomic DNA (gDIG5:dig5) on agar plates (B) or in soil (C). (D) Expression level of the DIG5 gene in the wild type and dig5 mutant seedlings. Shown are RNA blotting of total RNA probed with the radiolabeled DIG5 probe (upper panel) and loading control of ethidium bromide stained rRNA (lower panel).