Table 1.
Antiviral activities of flavonoids against swine viruses.
| Flavonoid | Structure | Virus | Treatment Time | Experimental Model | Effective Concentration | Inhibitory Phase | Mechanism | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) |
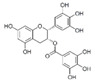
|
PRRSV | Pre | In vitro | 125 μM | Early phase | Block PRRSV binding to cells, reduce pro-inflammatory factors, and disturb lipid metabolism | [21,22,23,24] |
| PRV | Pre | In vivo/in vitro | 50 μM (in vitro) 40 mg/kg (in vivo) |
Multiple steps | Inhibit PRV adsorption, entry, and replication | [25,26] | ||
| PCV2 | Pre | In silico/in vitro | 100 μM | Early phase | Interacts with heparan sulfate to competitively inhibit capsid binding | [27] | ||
| H9N2 | Post | In vivo | 10 mg/kg | Multiple steps | Reduce Organs damage, inflammation, and virus titer | [28] | ||
| quercetin |
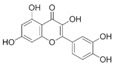
|
PRRSV | Post | In vivo | 10 mg/kg 100 μM in vivo |
Multiple steps | Cross protective efficacy and inhibit the activity of Hsp70 | [29,30] |
| PEDV | Pre | In vitro | 100 μM | Early phase | Inhibit the activity of PEDV 3CL protease | [31,32,33,34] | ||
| PRV | Pre Simultaneity |
In vitro In vivo |
50 μM (in vitro) 1.51 μg (in vivo) |
Early phase | Interacting with the viral gD protein. Reducing the secretion of reactive oxygen species induced by PRV. |
[35,36] | ||
| kaempferol |
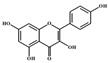
|
ASFV | Simultaneity Post |
In vitro | 20 μg/mL | Early phase | Induced autophagy | [37] |
| PRV | In vitro | 240 mg/kg | Early phase | Reduced the expression level of viral IE180 and inhibit viral replication | [25] | |||
| H9N2 | Post | In vivo | 15 mg/kg | Later phase | Inhibit the NF-κB and MAPKs pathways mediated by TLR4/MyD88 NF-κB | [38] | ||
| hyperoside |
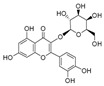
|
PEDV | Pre | in vitro | 20 μM | Later phase | Inhibited N protein-induced S phase cell cycle arrest | [39] |
| rutin |
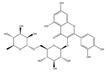
|
PRRSV | Post | In vitro | 7.8 μg/mL | Later phase | Regulate inflammation and suppress PRRSV replication | [21] |
| PRV | Post | In vitro | 40 μg/mL | Later phase | Inhibit the activation of NF-κB and MAPK pathways | [40] | ||
| total flavonoids of S. suberectus Dunn (TFSD) | - | PCV2 | Post | In vitro/In vivo | 50–100 μg/mL (in vitro)/ 50–100 mg/kg (in vivo) |
Later phase | Anti-oxidation and immunomodulatory effects | [41,42] |
| (+)-catechin |
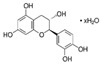
|
TGEV | Post | In vitro | 80 μM | Later phase | Anti-oxidation | [43,44] |
| myricetin |
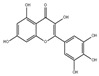
|
ASFV | Simultaneity | In vitro | 20 μM | Early phase | Interaction of 3, 4, 5-trihydroxyphenyl with ASFV protease | [45] |
| myricitrin |
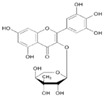
|
ASFV | Simultaneity | In vitro | 40 μM | Later phase | Interaction of 3, 4, 5-trihydroxyphenyl with ASFV protease | [45] |
| genistein |
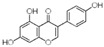
|
ASFV | Pre | In vitro | 50 μM | Early phase | Disrupt the synthesis of viral DNA | [46] |
| genkwanin |
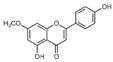
|
ASFV | Simultaneity | In silico/in vitro | 40 μM | Early phase, later phase | Inhibition of ASFV entry and release phases | [47,48] |
| apigenin |
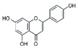
|
ASFV | Pre | In vitro | 50 μM | Early phase, later phase | Expression of 25-kD virus protein was inhibited | [47,48] |
| quercetin 7-rhamnoside (Q7R) | - | PEDV | Simultaneity | In vitro | 10 μg/mL | Early phase | Inhibit the early stage of viral replication | [34] |
| chalcone | - | H1N1 | Pre | In vitro | 2.49 ± 0.14 μg/mL | Later phase | Noncompetitive inhibitors of H1N1 neuraminidase | [49,50,51] |
| Isobavachalcone (IBC) |
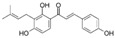
|
PRRSV | Post | In vitro | <15 μM | Later phase | Interference with RNA synthesis | [52] |
| PRV | Simultaneity | In vitro | 25.6 μM | Later phase | PRV replication was inhibited at the intercellular fusion stage | [53] | ||
| Xanthohumol (Xn) |
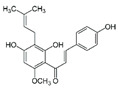
|
PRRSV | Pre | In vivo/in vitro | 15 μM | Later phase | Nrf2-HMOX1 axis | [54,55] |
| Isoflavones (ISF) | PRRSV | Post | In vivo | 1600 mg/kg | Later phase | Supported immune responses | [56,57,58] | |
| Puerarin | PEDV | Post | In vivo | 0.5 mg/kg | Later phase | Alleviate systemic inflammation | [59,60] |
