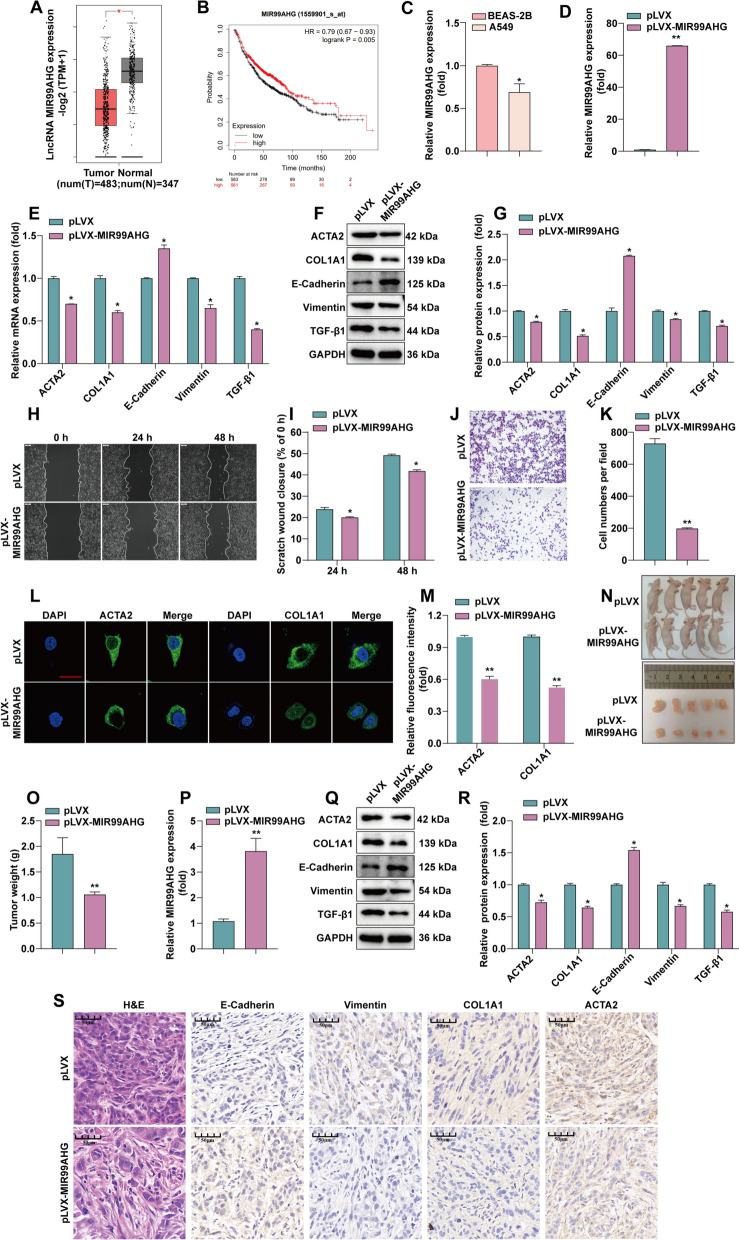
Fig. 1.
Overexpression of MIR99AHG suppresses EMT and fibrosis. A Analysis of LncRNA MIR99AHG expression in LUAD and normal lung tissues using the GEPIA database. B Analysis of the relationship between LncRNA MIR99AHG expression and survival of LUAD patients using the Kaplan–Meier plotter. C RT-qPCR detection of LncRNA MIR99AHG expression. D RT-qPCR to detect the stable overexpression efficiency of LncRNA MIR99AHG. E RT-qPCR to detect the expression of E-Cadherin, Vimentin, ACTA2 and COL1A1 after overexpression of LncRNA MIR99AHG. F, G The protein expression of TGF-β1, E-Cadherin, Vimentin, ACTA2 and COL1A1 was detected by WB and statistically quantified by ImageJ software. H, I After overexpression of LncRNA MIR99AHG, cell migration was monitored by wound scratch assay. Statistical data are shown. J, K After overexpression of LncRNA MIR99AHG, cell invasion was measured by invasion assay. Cell invasion was determined by invasion assay and counted by ImageJ counting. L, M Immunofluorescence assay was performed to detect the expression of fibrosis-related proteins after overexpression of LncRNA MIR99AHG. Statistical data are shown. N Subcutaneous tumorigenesis demonstration in nude mouse. O Tumor weights were represented as the means of tumor weights ± SD. P RT-qPCR to confirm the overexpression of LncRNA MIR99AHG in tumor tissues. Q, R WB to detect the expression of TGF-β1, E-Cadherin, Vimentin, ACTA2 and COL1A1 in MIR99AHG stabled overexpression tumor tissues. Statistical data are shown. S The tumor sections underwent IHC staining and H&E staining. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01