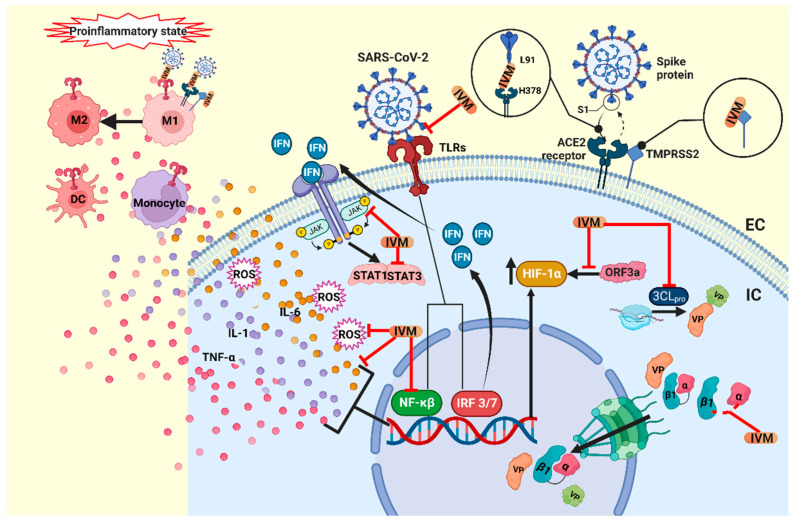
Figure 2.
Proposed mechanism of action of ivermectin in COVID-19. IVM blocks the binding complex of the SARS-CoV-2 S protein and the ACE2 receptor, and additionally it blocks the TMPRSS2 protein, inhibiting viral entry into the host cell. IVM could also inhibit the TLR receptors and block NF-κβ, inhibiting the production of the cytokines TNF-α, IL-1 and IL-6 and ROS. TLR also activates IRF3 and IRF7, which initiate the production of type-I and -III IFNs. IFNs activate the JAK/STAT pathway, while IVM can lower the expression of JAK2 and the activity of STAT3. Moreover, in the cytosol, IVM blocks the 3CLpro, the main protease that participates in the viral replication, and blocks the importin complex α/β1 that transports the VP to the nucleus. Furthermore, IVM blocks the overexpression of HIF-1α, induced by the viral protein ORF3a. IVM has also been shown to mitigate the proinflammatory state, where the cytokine storm activates the participation of monocytes, dendritic cells and macrophages, and IVM also promotes the polarization of M2 macrophages over M1. IVM, ivermectin; IC, intracellular; EC, extracellular; VP, viral protein; TLRs, toll-like receptors; NF-κβ, nuclear factor-kappa beta; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-alpha; IL-1, interleukin-1, IL-6; interleukin-6; ROS, reactive oxygen species; IRF 3/7, interferon regulatory factors; DC, dendritic cells; M1, M1 macrophage; M2, M2 macrophage; 3CLpro, 3-chymotrypsin-like protease. Created with BioRender.com.