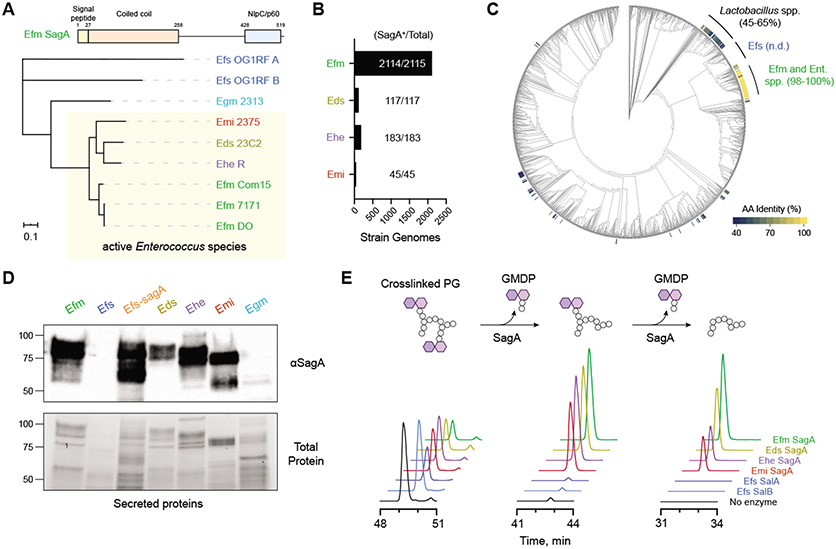
Fig. 2. Protective enterococci express and secrete active orthologs of the peptidoglycan NlpC/p60 hydrolase SagA.
(A) Domain structure and unrooted phylogenetic clustering of putative SagA ortholog protein sequences identified by global peptidoglycan peptidase analysis of enterococci species and strains along with the closest entries from E. gallinarum (Egm) and E. faecalis (Efs) based on IQ-Tree analysis. Numbers above each domain denote amino acid residue boundaries. Active strains are indicated by the yellow box. Scale bar represents sequence distance. (B) Bar plot and quantification of Enterococcus genomes containing SagA orthologs. (C) Cladogram of Human Microbiome Project isolates organized by 16S rRNA homology with heat map indicating amino acid (AA) sequence identity of putative SagA orthologs. n.d. = not detected; Ent. spp. = Enterococcus strains without an assigned species name. (D) Western blot detection of secreted SagA orthologs harvested from overnight cultures of the indicated enterococci using antiserum raised against E. faecium (Efm) Com15 SagA. Bottom panel shows total protein loading. Numbers indicate estimated molecular weight (kDa). (E) In vitro activity of purified SagA orthologs. Data are shown as extracted LC-MS ion chromatograms of a crosslinked peptidoglycan substrate and two iterative hydrolysis products after incubating a mixture of peptidoglycan fragments with purified SagA orthologs from the indicated species for 16 hours at 37 °C. Peak heights are shown as relative intensity of ion abundance, and all chromatograms are shown on the same scale.