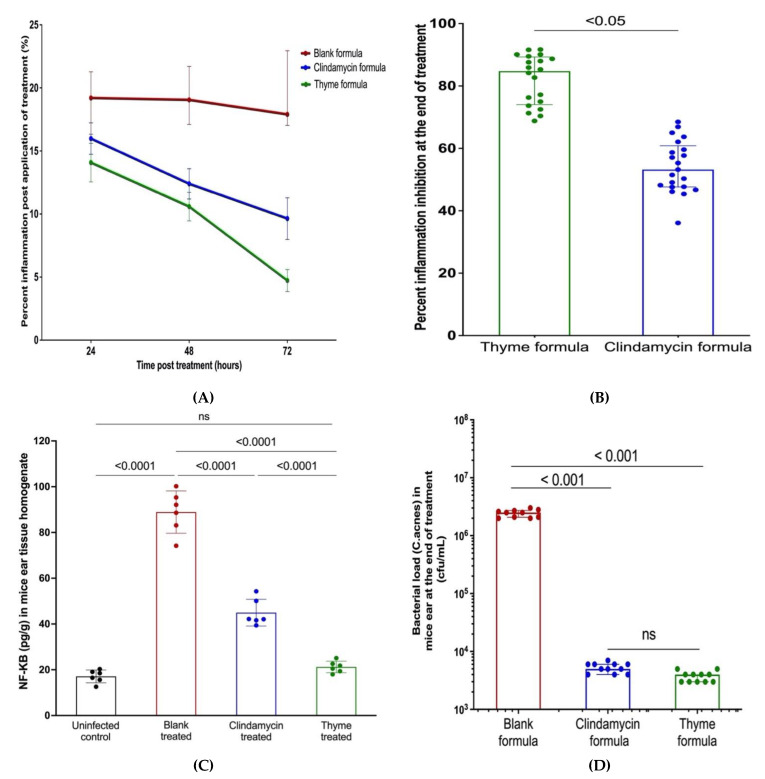
Figure 9.
(A) Rate of inhibition of inflammation by thyme EO nanoemulsion and controls in acne mouse model showing that the reduction in mice ear thickness post-treatment with thyme EO was superior to clindamycin as a positive control; (B) Percent of inflammation inhibition at the end of treatment showing thyme EO nanoemulsion resulting in more than 80% inhibition of inflammation at the end of the treatment period, while clindamycin resulted in a reduction in inflammation by 55%. Mann–Whitney test was performed, p-value < 0.05; (C) Thyme EO resulted in a 5-fold reduction in NF-κB levels while clindamycin caused only 2.5-fold reduction in the transcription protein. Ordinary one-way ANOVA—Tukey’s multiple comparison test was performed, p-value < 0.001; (D) In vivo antimicrobial activity of thyme EO nanoemulsion and clindamycin control exerting potent antimicrobial activity against C. acnes as the bacterial load was reduced to ~103 cfu/mL in both groups, while the bacterial load in the blank formula-treated mice group (negative control) was kept at 105 cfu/mL. Ordinary one-way ANOVA—Tukey’s multiple comparison test was performed, p-value < 0.0001. Data are represented as mean ± SD of three independent experiments.