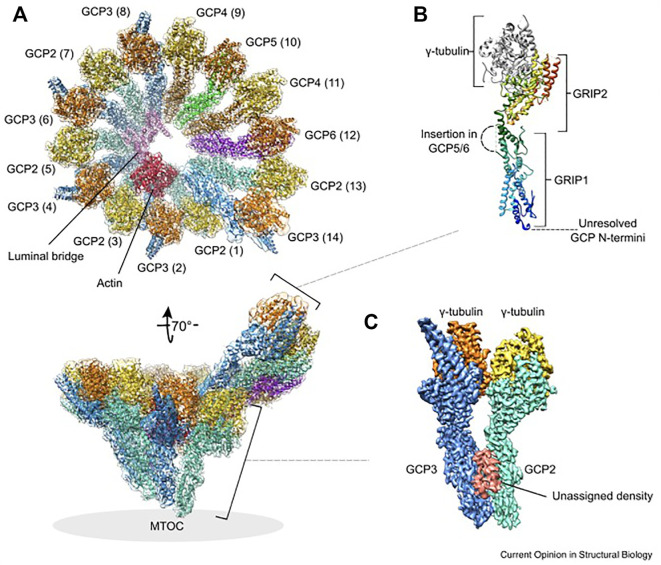
FIGURE 2.
Structure and molecular architecture of human γ-TuRC. (A) General architecture of the left-handed γ-TuRC spiral as determined by cryo-EM single-particle analysis, resolution 3.8 Å. γ-Tubulins (yellow, orange), GCP2 (aquamarine), GCP3 (blue), GCP4 (brown), GCP5 (green), GCP6 (purple), actin (red) and the luminal bridge (pink) are shown. The spokes (GCP-γ-tubulin heterodimers) are numbered (1–14 in brackets). In the tilted view, the approximate location of the MTOC is indicated. The orientation of subcomplexes shown in panel (B) and (C) is indicated. (B) General architecture of a GCP-γ-tubulin spoke. The GCP N-terminal GRIP1 and C-terminal GRIP2 domains are annotated. Unresolved GCP segments are indicated by dashed lines. GCP is shown in rainbow colors from N-terminus (blue) to the C-terminus (red). (C) Location of the unassigned density segment (red) present on each GCP(2–3) subcomplex of the human γ-TuRC. This figure was prepared using PDB 6V6S and EMD-21074. Reprinted by permission from Current Opinion in Structural Biology (Zupa et al., 2021).