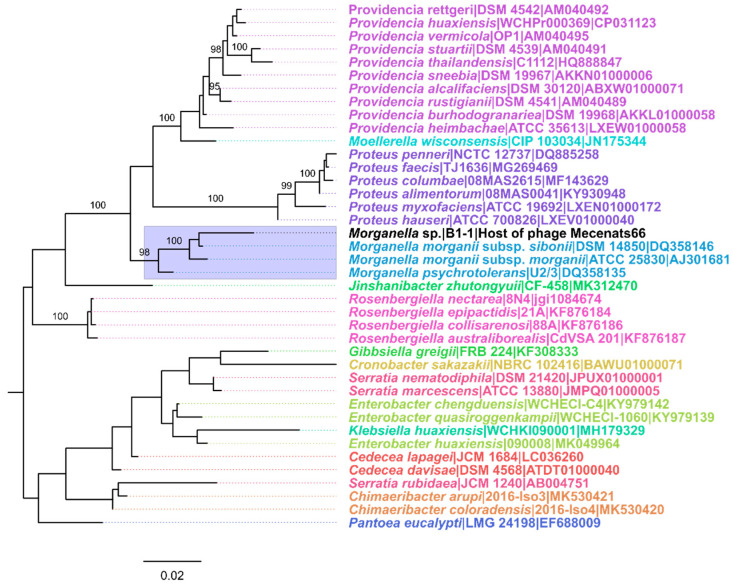
Figure 1.
The maximum-likelihood tree of the partial 16S rRNA gene sequences of the bacterial isolate B1-1 and closely-related bacterial species. The analysis involved 40 nucleotide sequences (16S rRNA gene sequences of isolate B1-1 and 39 other most closely related bacterial species identified). The tip labels correspond to the taxa and are in the format of “Species|Strain|Accession” and are colored based on the genus of the bacteria from which the sequence was derived. Isolate B1-1 is indicated by the black font, and the clade corresponding to the 16S rRNA sequences of bacterial genus Morganella representatives is highlighted in light blue. Input alignment had 1465 columns, 284 distinct patterns, 183 parsimony-informative, 41 singleton sites, and 1241 constant sites. The tree was built using TN + F + I + G4 as the best-fit substitution model. Near zero-length branches were collapsed into polytomies. The tree shown is midpoint rooted. The percentage of replicate trees in which the associated sequences clustered together in the ultrafast bootstrap (UFBoot; 1000 replicates) is shown next to the branches for branches with UFBoot support higher or equal to 95%. The tree is drawn to scale, branch lengths represent the number of nucleotide substitutions per site.