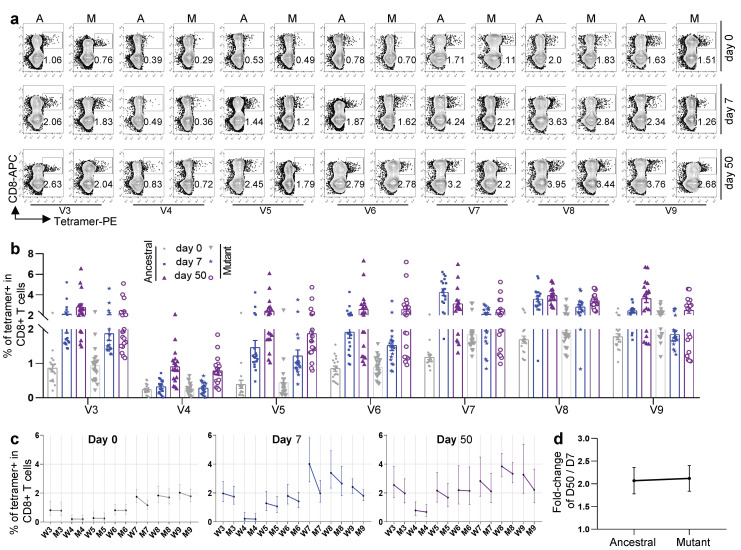
Figure 3.
Comparison and characterization of SARS-CoV-2 epitope-specific CD8 T cells between 7 and 50 days after the third dose. (a) Representative data for the detection of epitope-specific CD8 T cells in HLA-A2+ healthy donors before and after a third dose of inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine with tetramers prepared using SARS-CoV-2 epitopes. A: ancestral; M: mutant. Variant strain IDs are the same as listed in Table 1. The flow cytometry gating strategy is shown in (a). (b) Comparison of epitope-specific CD8 T cells between HLA-A2+ healthy young and old donors 0 (gray), 7 (blue), and 50 (purple) days after the third dose of inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine. Specific CD8 T cells were individually stained with tetramers prepared using ancestral and mutant SARS-CoV-2 epitopes. n = 18 per group. (c) Comparison of specific CD8 T cells between ancestral and mutant SARS-CoV-2 epitopes in HLA-A2+ donors before the third vaccination with the SARS-CoV-2 inactivated vaccine (left), 7 days (middle), and 50 days (right) after vaccination. Specific CD8 T cells were individually stained with tetramers prepared using ancestral and mutant SARS-CoV-2 epitopes. Variant strain IDs are the same as listed in Table 1. Paired ancestral and mutant epitopes are listed adjacently on the x-axis. Data shown are the mean ± SD. (d) Summary statistics of the detection fold-change of CD8 T cells specific to SARS-CoV-2 epitopes between 50 and 7 days after the third dose. Data shown are the mean ± SD.