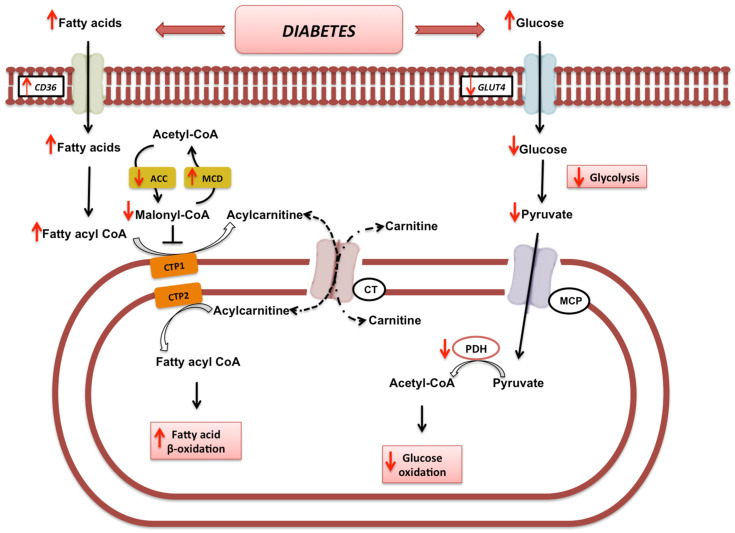
Figure 1.
Metabolic alterations in diabetic patients. At the molecular level, insulin resistance causes an increase in both plasma glucose and serum insulin levels, which lead to a reduction in glucose transporter type 4 (GLUT4), and a decrease in glucose uptake. These events lead to a reduction in the glycolysis pathway and glucose oxidation caused by the downregulation of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDH). The hyperglycaemia is associated with the concomitant increase in hematic fatty acid concentration and the consequent upregulation of fatty acids uptake and oxidation due to the decreased levels of malonyl CoA and the consequent activation of carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1 (CPT1). CD36—cluster of differentiation 36; ACC—Acetyl-CoA carboxylase; MCD—Malonyl-CoA decarboxylase; CTP1—carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1; CTP2—carnitine palmitoyltransferase 2; MCP—mitochondrial pyruvate carrier; CT—carnitine translocase; PDH—pyruvate dehydrogenase complex; GLUT4—glucose transporter type 4.