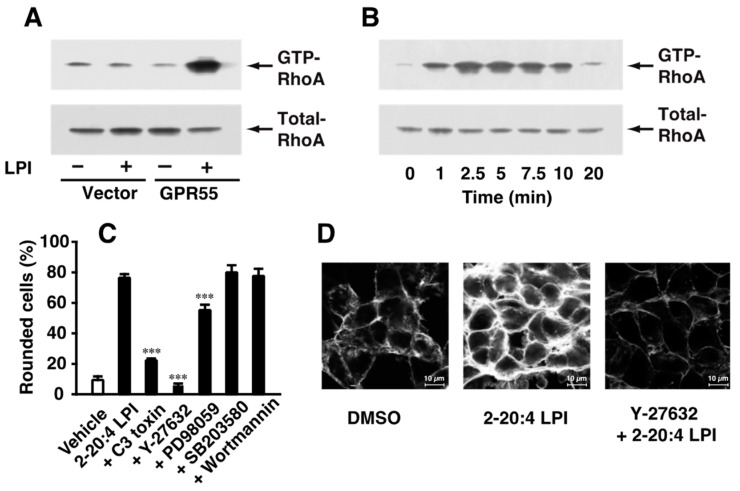
Figure 3.
Involvement of the activation of RhoA-ROCK in 2-arachidonoyl LPI-induced and GPR55-dependent cell rounding and stress fiber formation. (A) Activation of RhoA. Empty-vector-transfected or GPR55-expressing HEK293 cells were challenged with vehicle (DMSO) or 2-arachidonoyl LPI (1 µM) at 37 °C for 5 min. (B) Time course of RhoA activation. GPR55-expressing cells were challenged with 2-arachidonoyl LPI (1 µM) at 37 °C for the indicated periods. (C) Effects of various inhibitors on 2-arachidonoyl LPI-induced RhoA activation. GPR55-expressing cells were pretreated with vehicle, C3 toxin (20 µg/mL, 24 h), Y-27632 (20 µM, 1 h), wortmannin (500 nM, 1 h), PD98059 (20 µM, 1 h), or SB203580 (20 µM, 1 h) and then with 1 µM 2-arachidonoyl LPI for 5 min. Statistical analyses were performed with one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), followed by Tukey–Kramer multiple comparison test. The values are means ± SDs of five determinations. *** p < 0.001 versus 2-arachidonoyl LPI alone. (D) 2-Arachidonoyl LPI-induced stress fiber formation. Vehicle or Y-27632 (20 µM, 1 h)-treated GPR55-expressing cells were challenged with 1 µM 2-arachidonoyl LPI for 5 min. Scale bar, 10 μm. The results are representative of three independent experiments, which gave similar results (A,B,D).