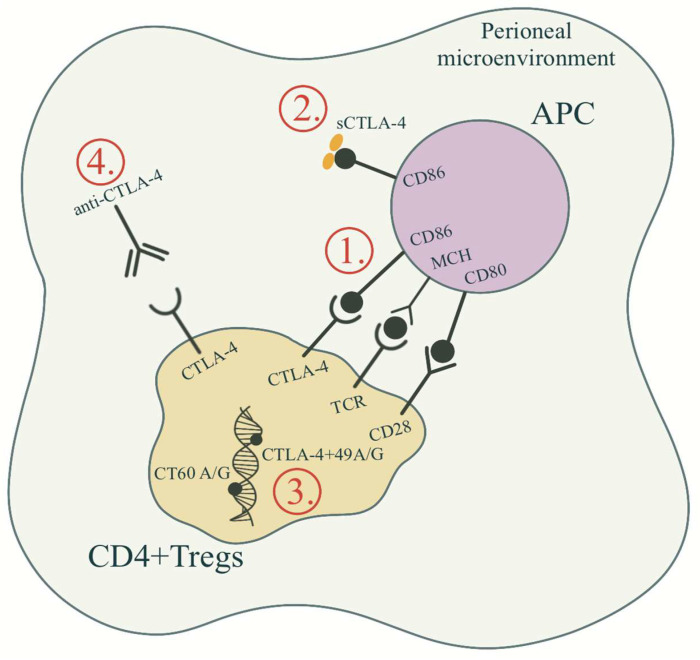
Figure 2.
The mechanisms of CTLA4 involvement in the pathogenesis of endometriosis. (1) The CTLA4 expressed on the surface of T cells involved in inhibitory co-stimulatory signal in T cell proliferation; (2) Higher serum and peritoneal soluble form of CTLA4 (sCTLA4) found in advanced endometriosis and related infertility; (3) CTLA4 gene polymorphisms not associated with the pathogenesis of endometriosis; (4) Anti-CTLA4 antibodies in mouse endometriosis model found to reduce the number of Treg cells and thus inhibit proliferation and invasion of ectopic endometrium. (Original illustration).