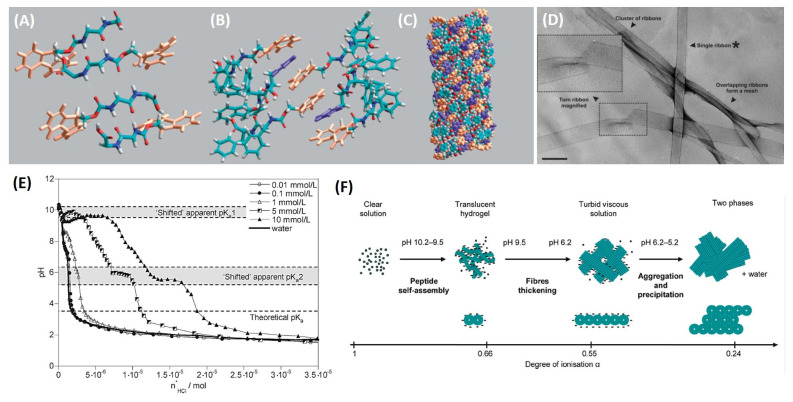
Figure 2.
Structural model of Fmoc-FF peptides. (A) Dipeptide copies are arranged into β-sheet with an antiparallel orientation of β-strands. (B) π-stacked pairs due to the interlocking of fluorenyl groups from alternate β-sheets. (C) The final model obtained by energy minimization. In the model Fmoc and the phenyl groups are coloured in orange and in purple, respectively. (D) Transmission electron microscopy of Fmoc-FF xerogel (scale bar = 500 Å); the ribbon asterixed by authors was selected for other morphological analysis. (E) Titration curves of water and Fmoc-FF samples at different peptide concentrations (0.01, 0.1, 1, 5, and 10 mmol/L). (F) Mechanism proposed to explain the formation of Fmoc-FF aggregates as consequence of the pH decrease (figure adapted with permission for Refs. [53,54], Copyright 2009 American Chemical Society).