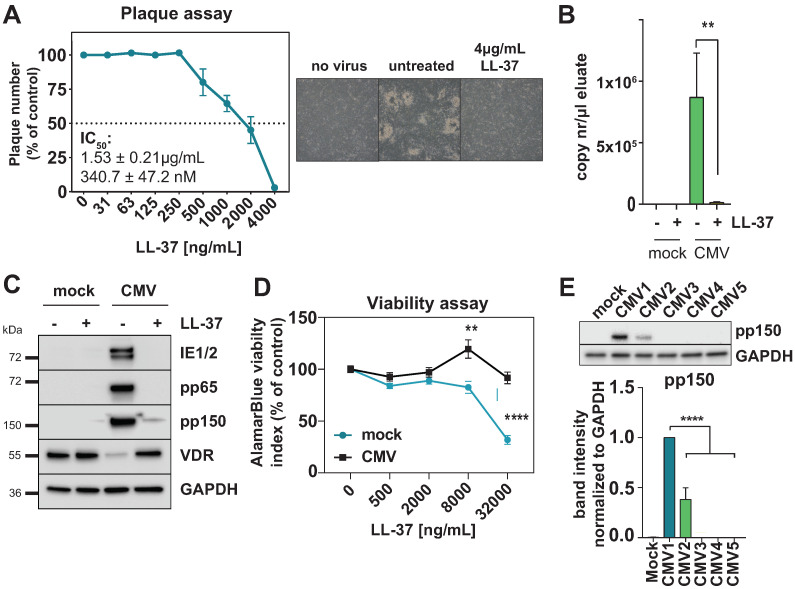
Figure 6.
Cathelicidin inhibits HCMV replication. (A) Plaque reduction assay of HFF infected with HCMV AD169 pre-treated with increasing amounts of LL-37; percentage compared to DMSO control is shown (n = 2). Light microscope pictures of representative areas for the non-infected control, virus control and maximum LL-37 concentration are shown on the right. (B) Intracellular CMV DNA was detected in lysates from infected HFF at 72 h p.i. and 4 μg/mL LL-37 (where indicated) using primers specific for the UL83 (pp65) gene. Quantification of copy numbers per measured sample were calculated by interpolation of values against a 5-point standard curve of pcDNA-pp65 plasmid dilutions. (C) Western blot showing abundance of the indicated proteins in whole cell lysate (WCL) from mock-infected or HCMV-infected HFF at 96 h p.i with or without treatment with 4 μg/mL LL-37 peptide. Representative of three independent experiments. (D) AlamarBlue viability assay showing reduction in the viability index in mock- and CMV-infected cells treated with up to 32 μg/mL LL-37 compared to the respective untreated control. (E) Western blot (left) and quantification (right) of pp150 relative protein abundance in cell lysates harvested at 96 h p.i. at MOI 0.05. HFF cells were either left untreated (mock, CMV1) or LL-37-treatment conditions (4 μg/mL, CMV2 to CMV5). LL-37 was either added to the medium 2 h after inoculation (CMV2), or incubated for 1h with the cells prior to infection and then removed before adding the inoculum (CMV3). CMV4: LL-37 was incubated for 1h with the viral supernatant before inoculating the cells, or LL-37 was added to both the cells and viral supernatant (CMV5).