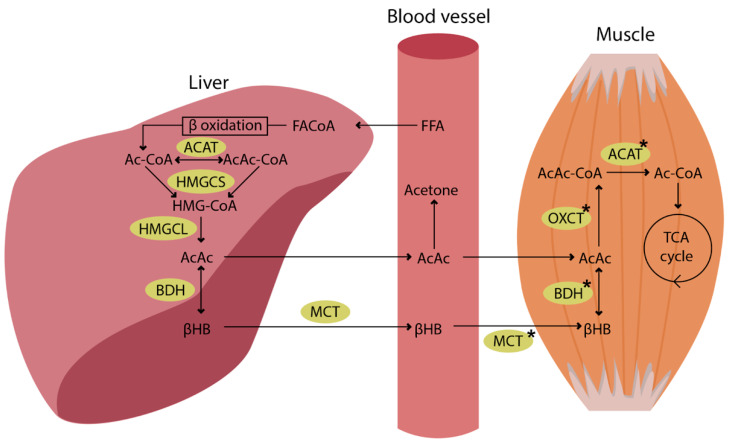
Figure 1.
Ketogenesis in the liver and ketolysis in the muscle (for details see [14]). FFAs are transported to the liver and converted to fatty acyl CoA (FA-CoA). The next step after β-oxidation is condensation of Ac-CoA molecules to acetoacetyl CoA (AcAc-CoA) by mitochondrial thiolase activity of Ac-CoA acetyltransferase (ACAT). Then, in a reaction with hydroxymethylglutaryl CoA synthase (HMGCS) generates hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA (HMG-CoA). HMG-CoA decomposes to AcAc by HMG-CoA lyase (HMGCL). AcAc can be released to the circulation, but most of it is reduced to βHB by 3-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase (BDH). βHB can undergo interconversion with AcAc in the liver and in other tissues after its uptake from the blood. Succinyl-CoA:3-oxoacid CoA transferase (OXCT) catalyses the generation of AcAc-CoA from AcAc and succinyl-CoA. Finally, AcAc-CoA is cleaved to Ac-CoA by ACAT, and Ac-CoA is incorporated into the TCA cycle. The asterisk (*) indicates protein content and enzyme activity that are higher in the exercise-trained skeletal muscle.