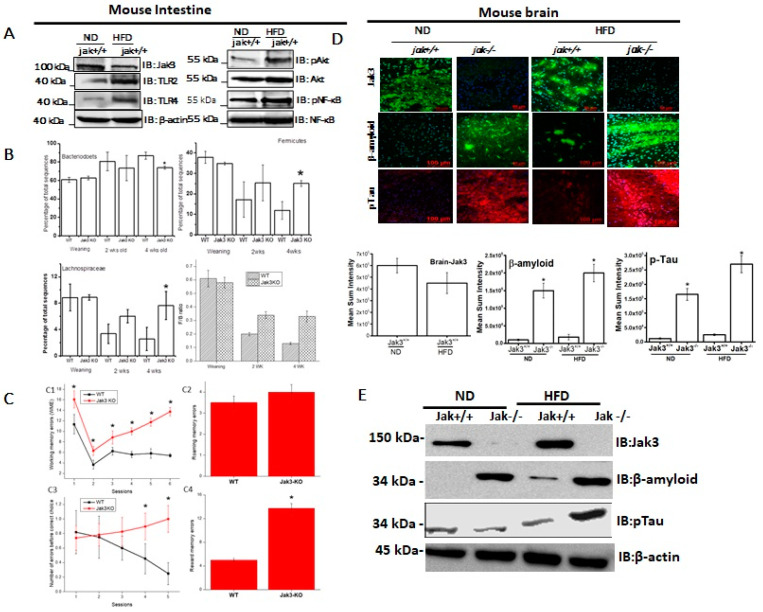
Figure 1.
High-fat diet (HFD) reduces intestinal expression of Jak3, and Jak3 deficiency in mice leads to colonic dysbiosis, cognitive impairment and accumulation of β-Amyloid and pTau in obese mouse brain. (A) Colons from normal diet (ND) and HFD-fed mice were excised out, and Western blot analysis was performed using the tissue lysates for the indicated proteins using β-actin as controls. Representative blots (n = 3) are shown. (B) Jak3 deficiency promotes gut dysbiosis. Gut microbiome composition was determined using a commercial facility through 16sRNA pyrosequencing of fecal DNA samples from co-housed WT and Jak3-KO littermates (n = 10 each group). The time courses of changes in fecal microbiota from WT and Jak3-KO mice are shown through the shift in the relative abundance of specific taxa (Upper panels; UP), specific family (Lower left panel; LLP), and the time courses of the relative shift in Firmicutes to Bacteroidetes ratio (F/B) (Lower right panel; LRP) are shown. Statistical analysis was performed using repeated measures paired group analysis of variance. Error bars represent +/−SEM. * indicate statistically significant differences compared to WT (ULP; p = 0.004, URP; p = 0.002, LLP; p = 0.001). (C) Jak3 deficiency promotes cognitive impairment. Automated elevated radial arm maze equipped with MazesoftTM Software was used to calculate the four parameters of cognitive assessments, viz., working memory errors (WME) (Upper left), roaming memory errors (RME) (Upper right), number of errors before a correct choice (EBCC) (Lower left) and reward memory errors (RWME) (Lower Right) over five sessions. A repeated-measure ANOVA on performances of age- and sex-matched wild-type (WT) littermate controls of Jak3-KO mice (n = 20 each group) are shown for each session (Upper and lower left panels) or an average of all the sessions (Upper and lower right panels). All the data are representative of three independent experiments. Values are mean ± S.D. * denotes p < 0.05 compared with WT mice. (Upper left; p = 0.002, Lower left; p = 0.004, Lower right; p = 0.001). (D) Jak3 deficiency promotes accumulation of β-Amyloid and pTau in mouse brain. Brain tissue sections from WT and corresponding Jak3-KO littermate mice fed with either ND or HFD were immunostained using β-amyloid or pTau or Jak3 primary antibodies followed by FITC- or Cy-3-conjugated secondary antibodies. Mounting media containing PI were used to visualize the nucleus. Representative images (n = 10) are shown (Lower panels). Quantifications of the intensities in the “upper panels” were performed using NikonR C1-plus imaging software, and the results were normalized against PI for Jak3 (Lower left), β-amyloid (Lower middle) and pTau (Lower right). Values are mean ± S.D. Asterisk denotes p < 0.05 compared with WT mice group. (Jak3 p = 0.003, β-amyloid p = 0.005, pTau p = 0.002). (E) Brain tissue lysates from the samples in “D” were used to perform IB in the presence of the indicated antibodies with β-actin as control. Representative blots (n = 3) are shown.