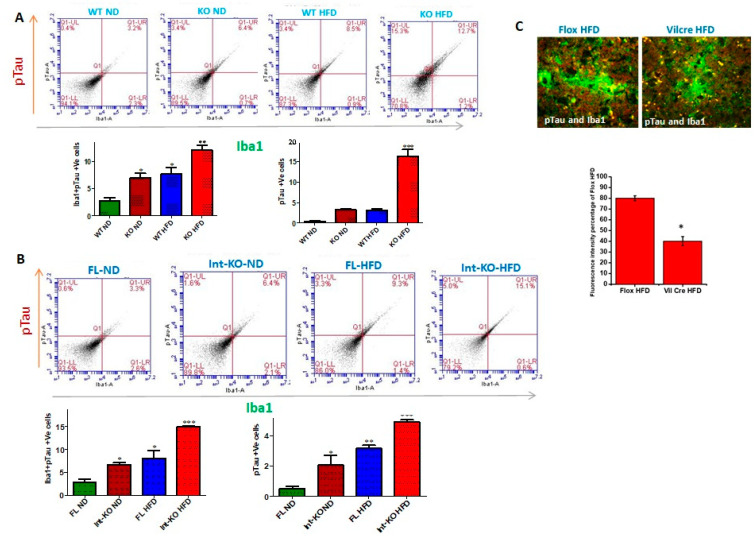
Figure 9.
Intestinal epithelial cell deficiency of Jak3 causes suppressed microglial Iba1 associated increased accumulation of pTau in the brain. (A,B), FACS analysis is presented as four quadrant dot plots to determine the impact of either global Jak3 deficiency (A) or IEC Jak3 deficiency (B) on microglial accumulation of pTau in the individual mouse brain tissues by determining the double positive cells (Quadrant:UR) for microglial marker Iba1 on the X axis and pTau on the Y axis in mice fed with either ND or HFD. The lower panels show the corresponding bar chart results following repeating (n = 5) the FACS experiments, and mean ± SD values are shown as bar graph for the comparative average cell counts for the indicated groups of mice. *, **, *** denotes p < 0.04 in all groups. (C) Microglial internalization of pTau is compromised in IEC-Jak3-deficient mice. Brain tissue sections from flox-Jak3-control littermate and IEC-Jak3-KO mice fed with HFD were co-immunostained using microglial marker Iba1 and pTau primary antibodies followed by FITC and Cy3 secondary antibodies, respectively, and merged images are shown to visualize the colocalized (yellow) cells. Representative images (n = 10) are shown (bottom bar graph). Nikon NIS elementR was used to count the double positive cells, and mean ± SD values are shown as bar graph for the comparative average double positive cells for the indicated groups of mice. * and ** denotes p < 0.04 in all groups.