Figure 21.
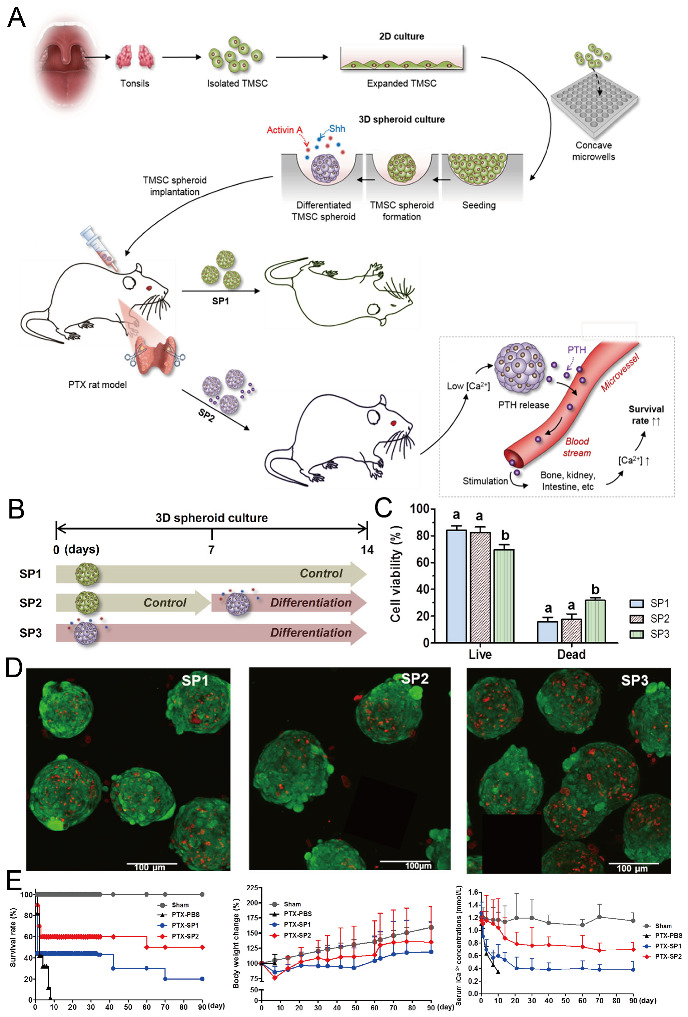
Formation of tonsil-derived mesenchymal stem cells (dTMSC) spheroids and their application in parathyroid tissue engineering [100]. (A) The schematic view of experimental procedures: at first, TMSCs were isolated from tonsils and then cultured in concave microwells; secondly, three different types of TMSC spheroids were formed under different culture conditions; thirdly, two types of TMSC spheroids were implanted into PTX rats to check their potential in hypoparathyroidism. (B) Three different types of TMSC spheroids: SP1 refers to the spheroids formed by culturing TMSCs in control medium for 14 days, SP2 refers to the spheroids formed by culturing TMSCs in control medium for the first 7 days and differentiation medium for the second 7 days, and SP3 refers to the spheroids formed by culturing TMSCs in differentiation medium for 14 days. (C) The viability of TMSCs in SP1, SP2, and SP3, respectively. (D) Fluorescent pictures of SP1 (left), SP2 (middle), and SP3 (right) stained by a live/dead assay, in which the green indicates the live cells and the red indicates the dead cells. (E) The comparison of survival rate (left), body weight change (middle) and serum iCa concentration (right) of PTX rats implanted with SP1 and SP2 in 90 days. PBS served as a negative control. Sham refers to rats with sham operation but no spheroid implantation.
