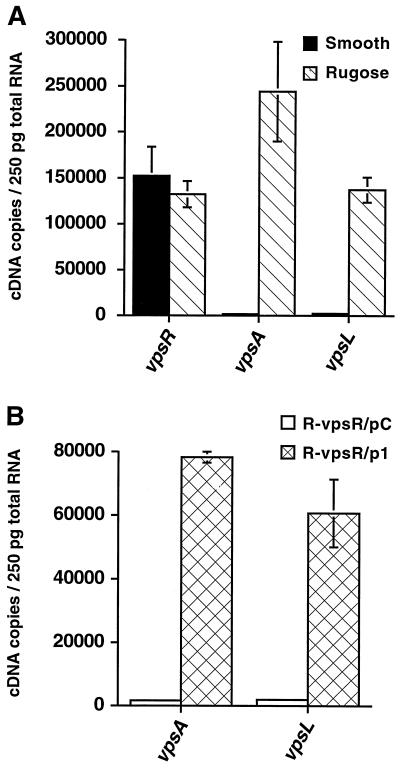
FIG. 4.
Transcriptional activity of vpsR and of the EPSETr biosynthetic gene cluster. (A) vpsR, vpsA, and vpsL mRNA abundance in wild-type smooth and rugose colonial variants. Standard curves for the vpsR, vpsA, and vpsL genes were generated by plotting the Ct value against the input DNA concentration, as described in Materials and Methods. Message abundance in exponentially growing wild-type smooth and rugose strains was calculated using the corresponding equations from the standard curves and the Ct values obtained after RT of total RNA, followed by real-time PCR amplification. vpsA and vpsL of the EPSETr biosynthetic gene cluster are strongly expressed in the rugose variant, but they are also expressed at low, basal levels in the smooth variant. Smooth and rugose variants expressed vpsR at equivalent levels. (B) Complementation of the vpsR mutant restores vpsA and vpsL expression. The vpsR mutant of the rugose colonial variant (denoted R-vpsR) was complemented with either a control plasmid (pC) or the control plasmid containing a wild-type copy of vpsR (p1). vpsA and vpsL mRNA abundances were determined during exponential growth for the complemented (R-vpsR/p1) and noncomplemented (R-vpsR/pC) mutant. Message abundance is expressed as the number of cDNA copies detected in 250 pg of total RNA.