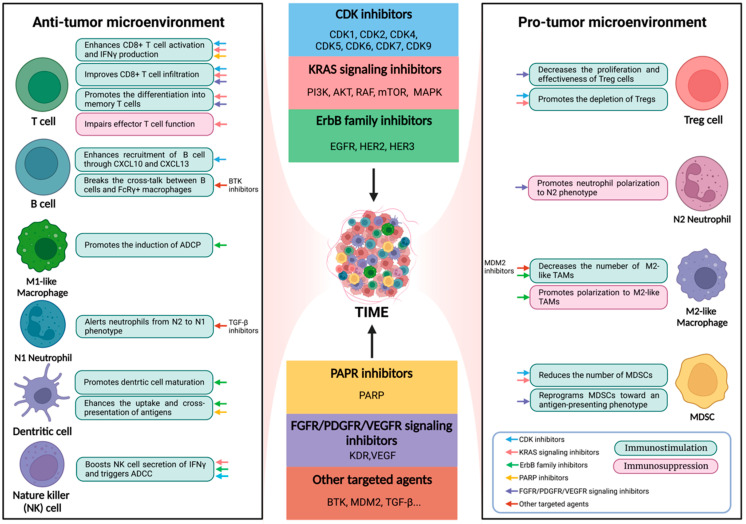
Figure 1.
Modulatory Effects of Targeted Therapy on Immune Cells. The molecularly targeted agents function as immunostimulatory (the green block diagram) or immunosuppressive (the red block diagram) modulators in TIME. The color of each little arrow matches the corresponding drug category in the middle of figure. ADCC, antibody-dependent cell cytotoxicity; ADCP, antibody-dependent cellular phagocytosis; AKT, V-akt murine thymoma viral oncogene homolog; BTK, Bruton’s tyrosine kinase; CDK, cycle-dependent kinase; EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; FGFR, fibroblast growth factor receptor; HER, human epidermal growth factor receptor; KDR, kinase insert domain receptor; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinases; MDM2, mouse double minute 2; MDSC, myeloid-derived suppressor cell; mTOR, mechanistic target of rapamycin; PARP, poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase; PDGFR, platelet-derived growth factors receptor; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase; TAM, tumor-associated macrophage; TIME, tumor immune microenvironment; TGF-β, transforming growth factor-β; Treg, regulatory T cell; VEGFR, vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (created with BioRender.com (accessed on 11 August 2022)).