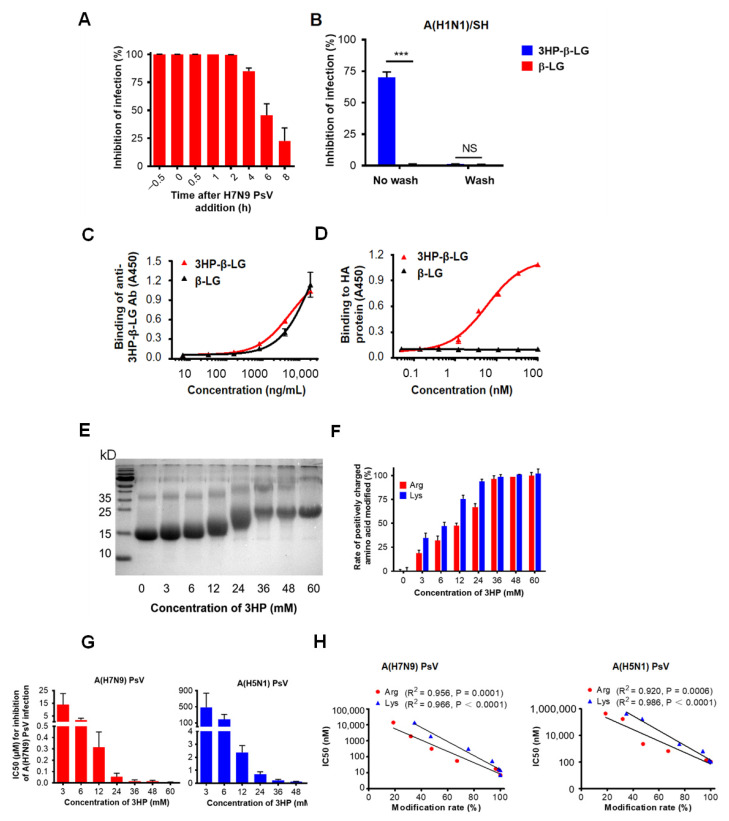
Figure 4.
Mechanism of 3HP-β-LG inhibiting influenza virus infection. (A) Time-of-addition assay. Influenza A(H7N9) PsV was added into MDCK cells at 0 h and 3HP-β-LG was added at −0.5, 0, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 6, and 8 h, respectively. Cell culture medium was substituted with fresh medium and tested 48 h post-infection. (B) Washout assay. After incubation with 3HP-β-LG, MDCK cells were not washed or were washed with DMEM before addition of influenza A(H1N1)/SH. Viral infectivity was measured as described in Materials and Methods. *** denotes p < 0.001; “NS” means no significance. (C) Binding of 3HP-β-LG and β-LG with anti-3HP-β-LG Ab as detected by ELISA. (D) Interaction of 3HP-β-LG and β-LG with influenza hemagglutinin (HA) protein detected by ELISA. The results are presented as mean ± SD. (E) SDS-PAGE analysis of β-LG modified with different concentration of 3HP. (F) Arginine modification rate (%) and lysine modification rate (%) of β-LG at different concentrations. (G) Inhibition of β-LG modified by different HP against influenza A(H7N9) and A(H5N1) PsVs. The “3 mM” means that β-LG was modified by 3HP at the concentration of 3 mM. Tests of different HP concentrations, including 3, 6, 12, 24, 36, 48, and 60 mM, respectively, were conducted and the inhibition of these concentrations against influenza A(H7N9) and A(H5N1) PsVs in MDCK cells was detected. Each sample was tested in triplicate and the data are displayed as mean ± SD. (H) The correlation between the modification rate of 3HP-β-LG and its antiviral activity (IC50) against influenza A(H7N9) PsV and A(H5N1) PsV is expressed by a linear equation. R2 and p values were calculated and are presented in the figure. Each sample was tested in triplicate and the data are shown as mean ± SD.