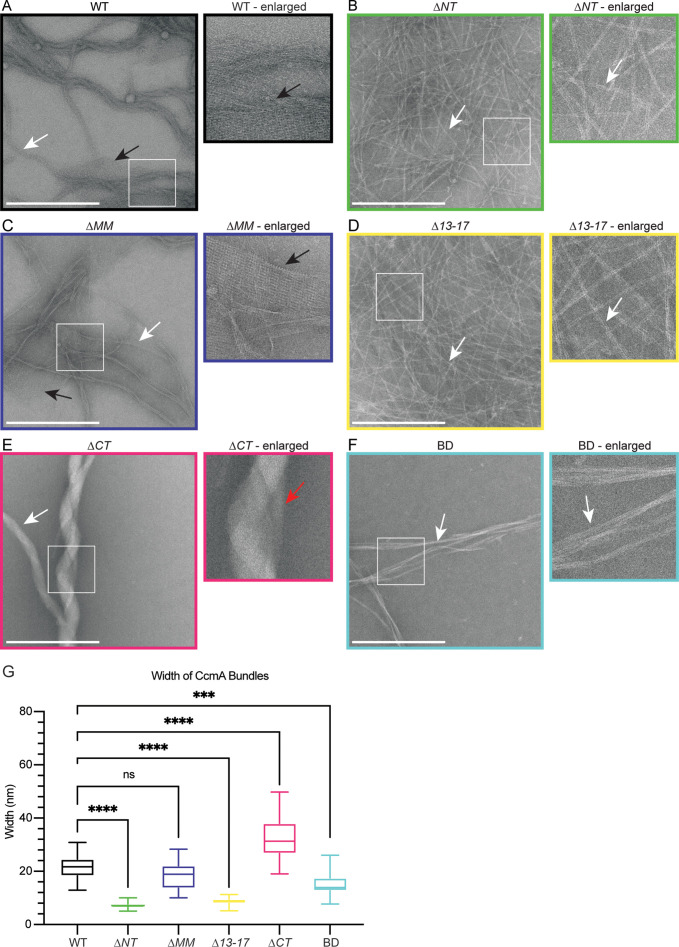
Figure 4. The bactofilin domain of CcmA is sufficient for in vitro polymerization while the terminal regions promote lateral polymer interactions.
(A–F) Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) of negative stained, purified CcmA, scale bars = 500 nm. White boxes indicate region of micrograph that is enlarged in panel to the right of original. White arrows indicate bundles of CcmA, black arrows indicate lattice structures, and red arrow indicates two bundles wrapping around each other. Data are representative of two independent biological replicates. (G) Box and whiskers plot displaying width of purified CcmA bundles and filaments. Median, min, max, 25th percentile, and 75th percentile are displayed. One-way ANOVA, Dunnett’s multiple-comparison test. ns p>0.5, ***p≤0.001, ****p≤0.0001. WT n = 24, ∆NT n = 29, ∆MM n = 25, ∆13–17 n = 31, ∆CT n = 24, BD n = 32.