Figure 8. Schematic depicting CcmA’s role in the helical cell shape complexes.
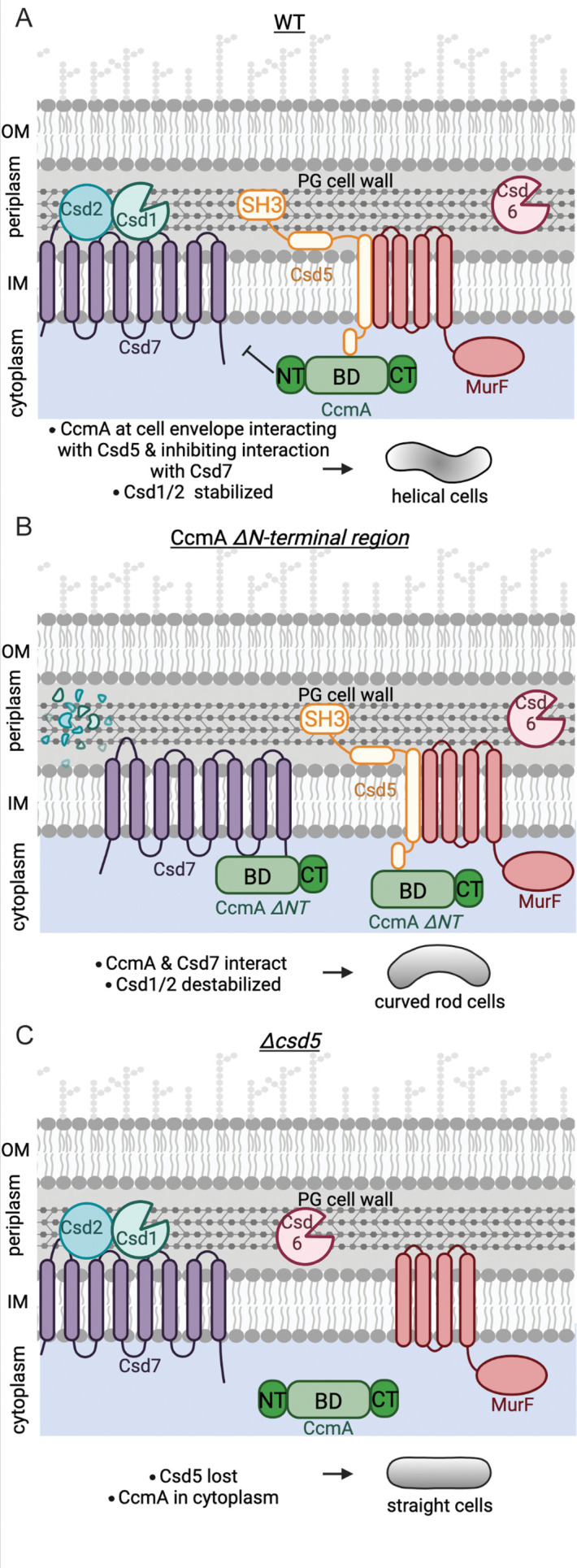
There are two protein complexes, one containing Csd5, MurF, and CcmA, and another containing Csd7, Csd1, and Csd2. (A) In WT cells, Csd5 recruits WT CcmA to the cell envelope via CcmA’s bactofilin domain. The N-terminal region of CcmA inhibits interaction with Csd7, allowing Csd1 to function and excluding Csd1 from the CcmA-Csd5-MurF complex. (B) In cells expressing CcmA ∆NT, Csd5 recruits ∆NT CcmA to the cell envelope via CcmA’s bactofilin domain. The bactofilin domain of CcmA now also binds to Csd7 in a separate complex, inhibiting Csd7 from stabilizing Csd1. (C) When Csd5 is absent, CcmA cannot localize to the cell envelope, MurF is not directed to a particular location. OM, outer membrane; IM, inner membrane. This figure was created using Biorender.com.
