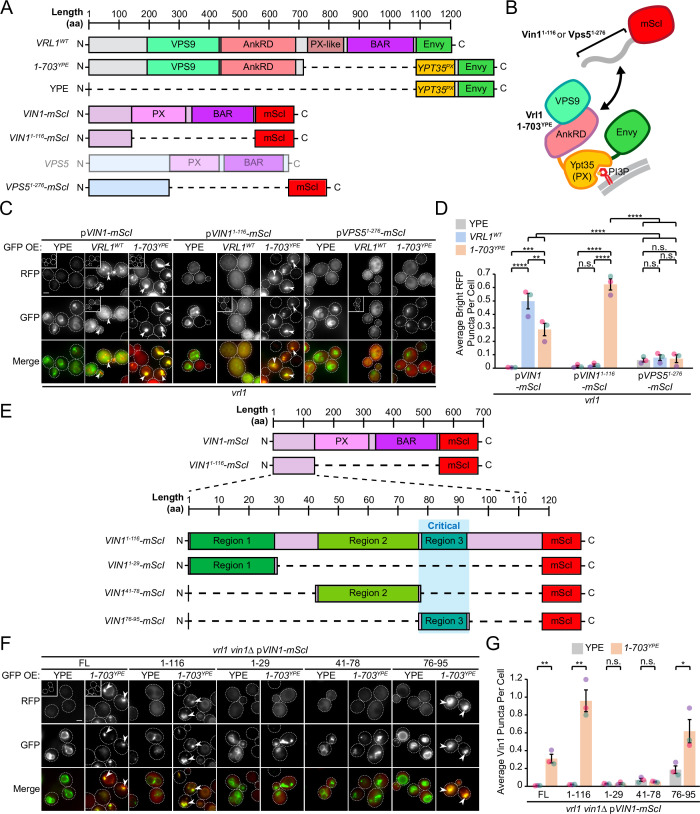
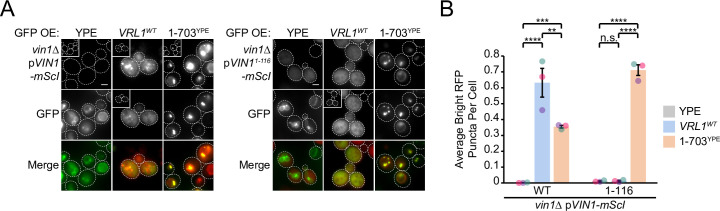
Figure 4. The Vrl1 AnkRD recognizes a small region of the Vin1 N-terminus.
(A) Schematic of constructs used in C, D. Full-length Vps5 was not tested but is shown for comparison. (B) Diagram of chimeric Vrl1 recruitment assay used to test for interactions with the unstructured N-terminus of either Vps5 (Vps51-276) or Vin1 (Vin11-116). (C) The AnkRD-containing Vrl1(1-703)YPE chimera recruits the N-terminus of Vin1, but not Vps5. Insets are scaled to match other images in the same channel (see Materials and methods for details). (D) Quantification of RFP puncta per cell in C. One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test; n=3, cells/strain/replicate ≥902; not significant, n.s.=p > 0.05, **=p < 0.01, ***=p < 0.001, ****=p < 0.0001. (E) Schematic of Vin1 N-terminal fragments used to map the Vrl1 recruitment site. (F) The AnkRD-containing Vrl1(1-703)YPE chimera recruits a small fragment of the Vin1 N-terminus. Insets are scaled to match other images in the same channel. (G) Quantification of Vin1-mScI puncta per cell in F. Two-tailed equal variance t tests; n=3, cells/strain/replicate ≥294; not significant, n.s.=p > 0.05, *=p < 0.05, **=p < 0.01. Scale bars, 2 µm. Error bars report SEM. OE, over-expressed. FL, full-length. WT, wild type. YPE, Ypt35(PX)-Envy.
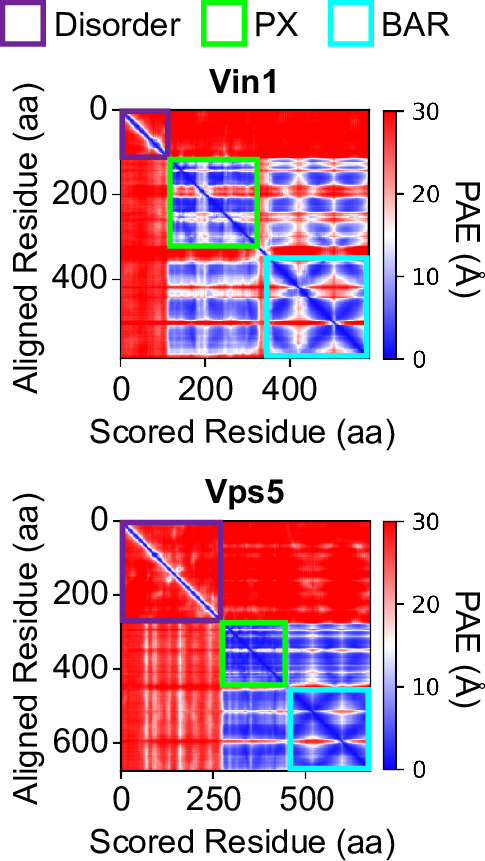
Figure 4—figure supplement 1. The N-terminal regions of Vin1 and Vps5 are predicted to be disordered.