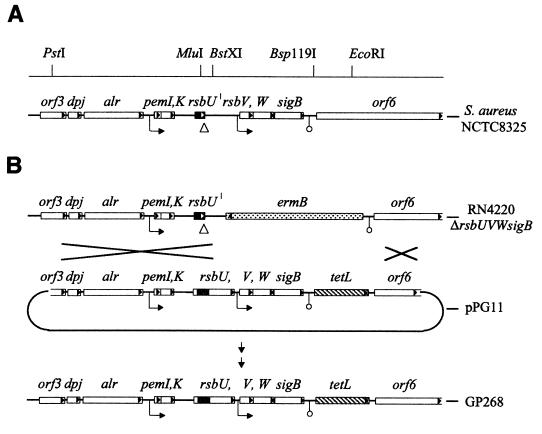
FIG. 1.
Genetic organization of the sigB operon. (A) Schematic representation of the sigB operon of S. aureus strain NCTC8325. Open reading frames, putative promoters (→), termination signals (○), and restriction sites used for construction of pPG11 are indicated. The 11-bp deletion within the rsbU gene of strain 8325, resulting in a truncated open reading frame for RsbU (solid area), is indicated by a triangle (▵). (B) Schematic representation of the rsbU+ construct pPG11 and of the strategy for the integration of this construct into the chromosome of S. aureus BB255. In plasmid pPG11, a 252-bp MluI-BstXI restriction fragment of the rsbU gene of strain COL including the 11 bp (shaded area) replaces the corresponding fragment of the rsbU allele from strain BB255 harboring the 11-bp deletion, leading to an open reading frame that encodes a functional RsbU protein. A tetL resistance gene was introduced as a selective marker downstream of the proposed termination signal of the sigB operon, in order not to disrupt the transcriptional control of this locus. Strain RN4220 ΔrsbUVWsigB, in which the major part of the sigB operon is replaced by an ermB resistance cassette (28), was used for electroporation to promote a double crossover of the modified sigB operon of the introduced pPG11 suicide plasmid upstream of the rsbU gene and downstream of the tetR gene. The chromosomal region of a positive transformant was phage transduced into strain BB255 to obtain strain GP268.