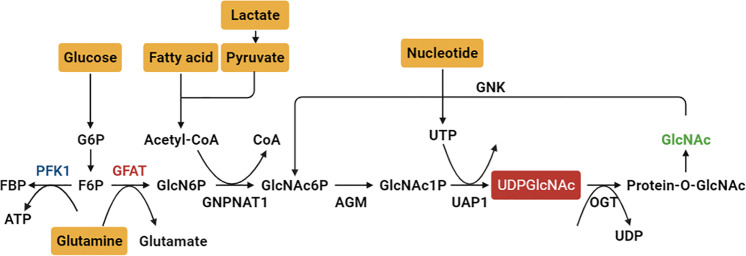
Fig. 2. The de novo hexosamine biosynthetic pathway (HBP) and GlcNAc salvage pathway integrate metabolic status from core metabolism intermediates, including glycolysis, fatty acid, amino acid and nucleotide metabolism, to generate uridine diphosphate-N-acetylglucosamine (UDP-GlcNAc).
Approximately 2–5% of cellular glucose enters the HBP to generate the end product UDP-GlcNAc. Glutamine:fructose-6-phosphate amidotransferase (GFAT) is the rate-limiting enzyme for the HBP. O-GlcNAc transferase (OGT) adds UDP-GlcNAc to target protein serine and threonine residues, and O-GlcNAcase (OGA) removes O-GlcNAc from O-GlcNAcylated proteins. The balance between the enzyme activities of phosphofructokinase (PFK) and GFAT through regulating GFAT may be crucial to direct the pathways. G6P glucose 6-phosphate, F6P fructose 6-phosphate, FBP fructose 1,6-phosphate, GlcN6P glucosamine-6-phosphate, GlcNAc6P N-acetylglucosamine-6-phosphate, GlcNAc1P N-acetylglucosamine-1-phosphate, GAT acetyl-CoA:D-glucosamine-6-phosphate N-acetyltransferase, AGM phosphor-N-acetylglucosamine mutase, AGX1 UDP-GlcNAc pyrophosphorylase, GNK GlcNAc kinase. The graph was created with BioRender.com.