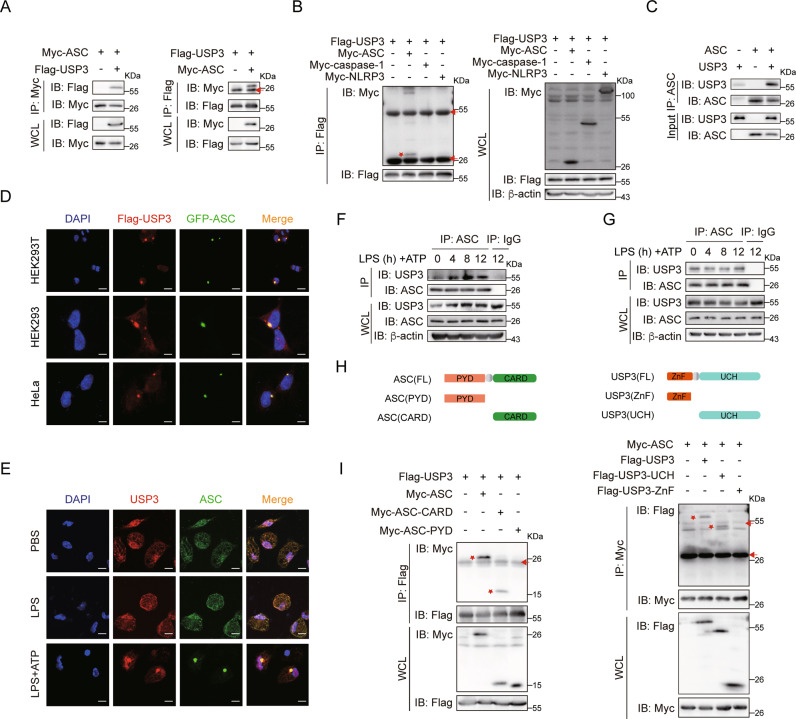
Fig. 1.
USP3 interacts with ASC. A Reciprocal immunoprecipitation analysis of the interaction between USP3 and ASC. HEK293T cells were transfected with the indicated plasmids for 36 h. The cell lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-Myc or anti-Flag antibody and then analyzed by immunoblotting. B Coimmunoprecipitation analysis of the interaction between USP3 and the indicated inflammasome components. C Coimmunoprecipitation analysis of the interaction between purified USP3 and ASC in vitro. Recombinant USP3 and ASC proteins were incubated for 60 min, and then the mixture was subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-ASC antibody followed by immunoblot analysis. D Colocalization of Flag-USP3 (red) with GFP-ASC (green) in HEK293T cells, HEK293 cells, and HeLa cells. Scale bar, 20 μm (top), 10 μm (middle and bottom). E Colocalization between USP3 and ASC in LPS-primed (8 h) PMs treated with ATP (30 min). Scale bars, 10 μm. Coimmunoprecipitation analysis of the interaction between endogenous USP3 and ASC with inflammatory stimulation. PMs in (F) or THP-1 cells in (G) were untreated or primed with LPS for the indicated time points followed by stimulation with ATP for 30 min, and then the cell lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-ASC antibody and immunoblot analysis. H Schematic diagram of ASC and USP3 and their truncation mutants. I Coimmunoprecipitation analysis of the interaction between ASC and USP3 truncation mutants. The experimental procedures in (B) and (I) were the same as those in (A). Data are representative of three independent experiments with similar results. Red arrow, IgG; red asterisk, indicated protein. β-Actin was used as a loading control