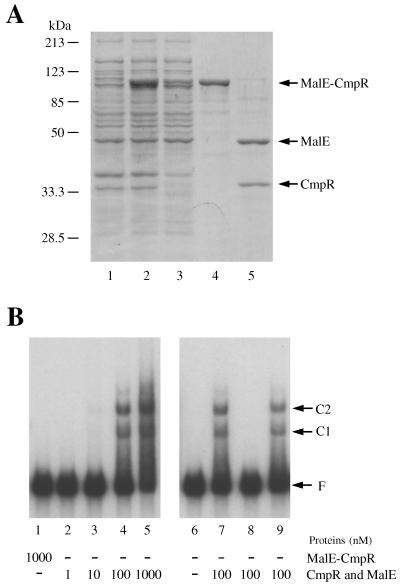
FIG. 3.
Preparation of recombinant CmpR and the mobility shift assays. (A) Expression in E. coli and purification of the MalE-CmpR fusion (lanes 1 to 4) and cleavage of the MalE-CmpR fusion with factor Xa (lane 5). Proteins were separated on a sodium dodecyl sulfate–10% polyacrylamide gel and stained with Coomassie brilliant blue. Lane 1, total protein from the E. coli expression strain before IPTG treatment; lane 2, total protein from the expression strain after 2-h treatment with IPTG; lane 3, soluble fraction from the IPTG-induced expression strain; lane 4, the protein purified on amylose resin; and lane 5, the MalE-CmpR fusion cleaved with factor Xa. (B) Mobility shift assays showing retardation in a 4% polyacrylamide gel of the 32P-labeled cmpR-cmpA intergenic segment by CmpR. Samples of the MalE-CmpR fusion (lane 1) and the MalE-CmpR fusion cleaved with factor Xa (lane 2 to 9) were added to the reaction mixtures to give the indicated final concentrations; 100-fold-excess amounts of nonlabeled cmpR-cmpA intergenic segment and a 0.7-kb segment of rbcL coding region were added to lanes 8 and 9, respectively, as competitors. C1 and C2, DNA-protein complexes; F, free probe.