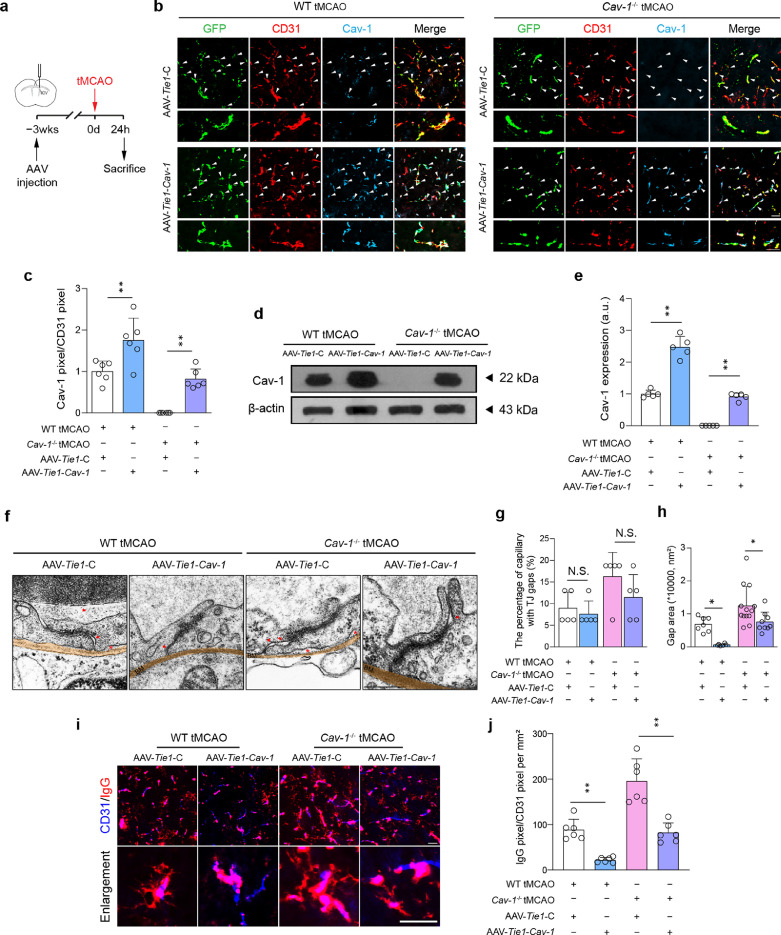
Figure 4.
Specific enhanced expression of Cav-1 in endothelial cells attenuates microvascular breakdown at tMCAO-24 h. (a) Experimental flow chart. (b) Representative fluorescent images of transfection of AAV with GFP (green) reporter into CD31+ microvessels (red) with enforced Cav-1 (light blue) expression at the peri-infarct tissue 24 h after surgery [quantified in (c); n = 6 in each group; mean ± S.D; **P < 0.01 vs. AAV-Tie1-C-transfected mice by one-way ANOVA with Tukey post hoc test]. (d, e) Immunoblotting and quantification showing the expression of Cav-1 in microvascular segments of peri-infarct area 24 h after surgery (a pool of 2 mice per sample, n = 5 samples in each group; mean ± S.D; **P < 0.01 vs. AAV-Tie1-C-transfected mice by one-way ANOVA with Tukey post hoc test). (f) TEM images and quantifications showing TJ gaps (red arrows) in the peri-infarct area [quantified in (g, h); n = 5 mice in each group. Sixteen capillaries were randomly chosen in each mouse; mean ± S.D; *P < 0.05 vs. AAV-Tie1-C-transfected mice by one-way ANOVA with Tukey post hoc test]. The red arrows indicate gaps between endothelial cells. The red asterisks indicate gaps between endothelial cells and basal membrane. (i-j) Representative images and quantification showing the IgG leakage at the peri-infarct tissue (n = 6 in each group; mean ± S.D; **P < 0.01 vs. AAV-Tie1-C-transfected mice by one-way ANOVA with Tukey post hoc test). Scale bar: 20 μm in (b, i) and 500 nm in (f). BM, basal membrane. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)