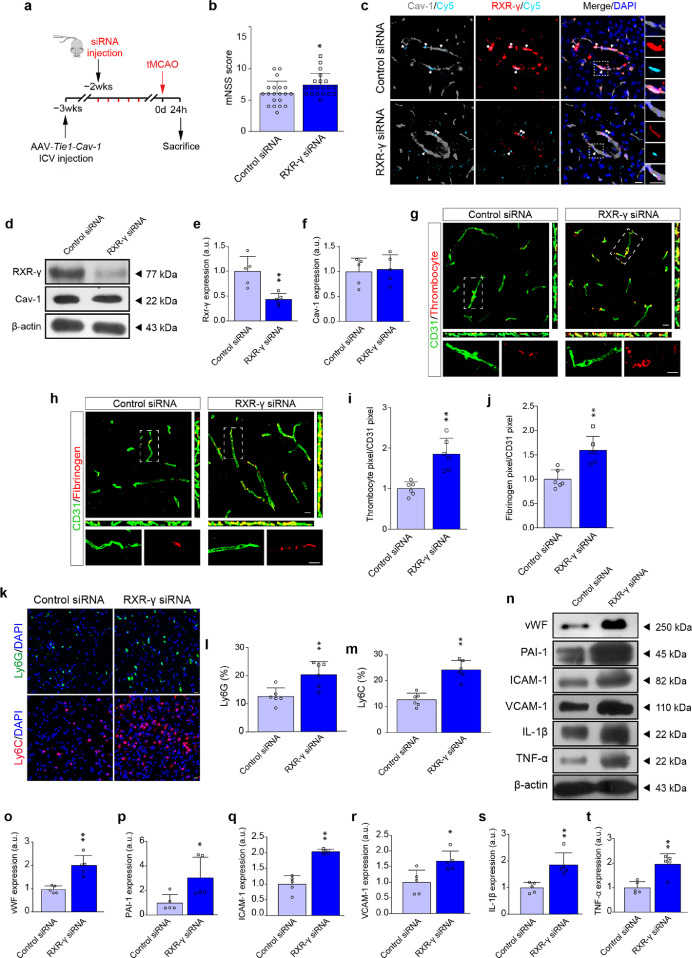
Figure 8.
RXR-γ is required in Cav-1-induced protection in cerebral I/R injury at 24 h. (a) Experimental flow chart. (b) The mNSS score of control or RXR-γ siRNA-transfected wild-type tMCAO mice at 24 h (n = 20 in each group; mean ± S.D; *P < 0.05 vs. control siRNA-injected mice by unpaired t-test). (c) Representative images showing the co-localization of siRNA (cyan), RXR-γ (red) and cav-1 (gray). (d–f) Immunoblotting and quantifications showing the expression of RXR-γ and Cav-1 in the microvascular segments 24 h after surgery (a pool of 2 mice per sample, n = 5 samples in each group; **P < 0.01 vs. control siRNA-injected mice by unpaired t-test). (g, h) Representative orthogonal views of Z-stack images showing the fibrinogen (red) and thrombocyte (red) in the CD31+ cerebral microvessels (green) 24 h after tMCAO [quantified in (i, j); n = 6 in each group; mean ± S.D; **P < 0.01 vs. control siRNA-treated mice by unpaired t-test]. (k) Representative immunofluorescent images showing the recruitment of Ly6G+ neutrophils and Ly6C+ monocytes at the peri-infarct area 24 h after tMCAO [quantified in (l, m); n = 6 in each group; mean ± S.D; **P < 0.01 vs. control siRNA-treated mice by unpaired t-test). (n–t) Immunoblotting and quantification showing the expression of vWF, PAI-1, ICAM-1, VCAM-1, TNF-α and IL-1β in brain microvascular segments 24 h after tMCAO (a pool of 2 mice per sample, n = 5 samples in each group; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 vs. control siRNA-injected mice by unpaired t-test). Scale bar: 10 μm. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)