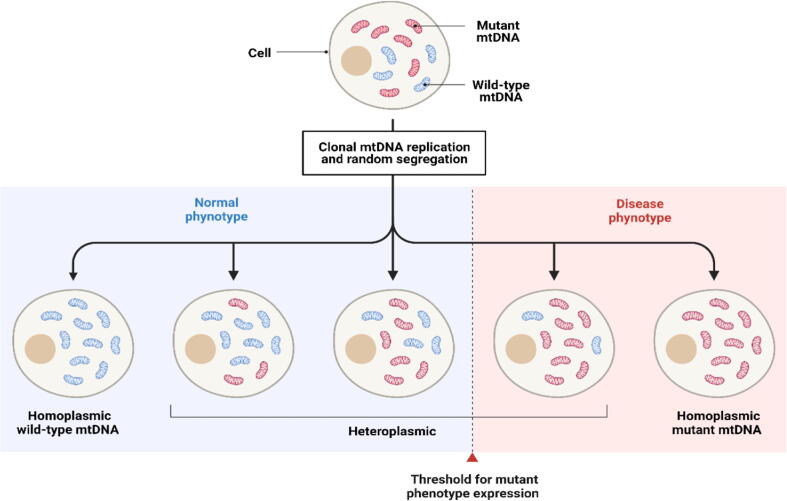
Fig. 2.
Schematic presentation of homoplasmic and heteroplasmic mitochondrial DNA. A single cell may obtain wild type copies of mtDNA (homoplasmy) or a mixture of mutant and wild-type mtDNA (heteroplasmy)). The proportion of mutant mtDNA copies determines the penetrance and severity of phenotype expression, and the cell will be affected if it exceeds a specific limit (threshold). Abbreviations: mtDNA, mitochondrial DNA. Created with Biorender.com.