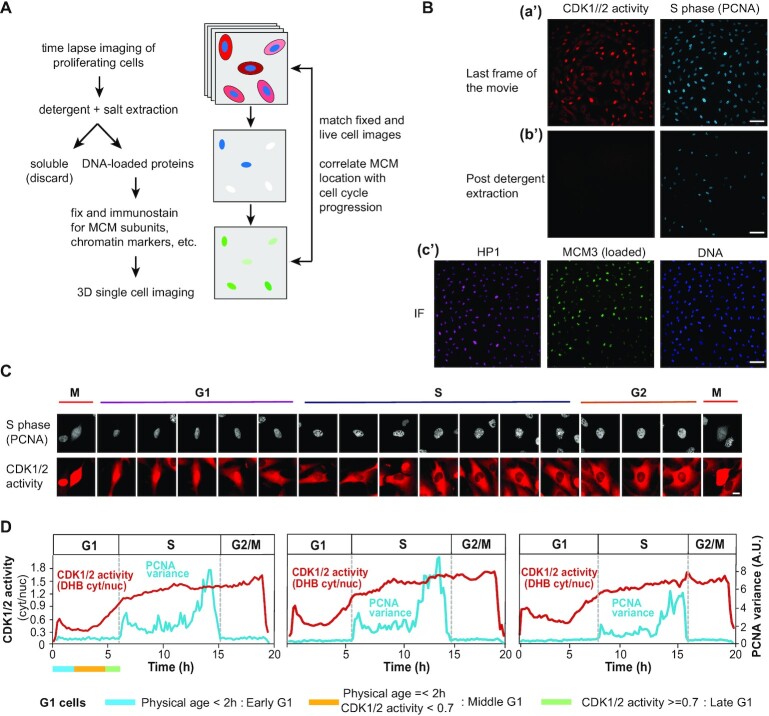
Figure 1.
An experimental system for analyzing subnuclear MCM loading dynamics within G1 phase. (A) Workflow. RPE1-hTert cells expressing PCNA-mTurquoise and the DHB-mCherry CDK1/2 activity reporter were subjected to time-lapse live-cell imaging, then soluble proteins were extracted with nonionic detergent and salt, and cells were fixed immediately after imaging for confocal immunofluorescence staining. (B) Representative example from combining live-cell imaging with fixed-cell imaging. (a′) Last frames from wide-field time-lapse imaging of cells expressing CDK1/2 activity and S phase reporters. (b′) Images collected with the same microscope settings after detergent extraction and fixation; scale bar represents 100 μm. (The CDK activity reporter is soluble.) (c′) Immunofluorescence of extracted and fixed cells after live-cell imaging. Cells were stained for bound HP1 (heterochromatin marker) and loaded MCM3 (MCM2–7 complex marker) and imaged by confocal microscopy; scale bar represents 100 μm. (C) Selected images from wide-field time-lapse imaging of one cell. Images were captured every 10 min for one cell cycle, and selected frames from one of the 50 cells are shown. The scale bar is 10 μm and applies to all images. Images were brightness/contrast adjusted. (D) Top: Traces of PCNA variance and CDK1/2 activity for three cells. CDK1/2 activity is the ratio of mean cytoplasmic DHB-mCherry reporter fluorescence divided by mean nuclear DHB-mCherry fluorescence. Hours are time since mitosis. Bottom: Defining G1 subphases by both physical age and CDK1/2 activity. G1 cells younger than 2 h after mitosis are early G1 cells; G1 cells older than 2 h with CDK activity <0.7 are middle G1 phase cells; and G1 phase cells with CDK activity ≥0.7 but not yet in S phase by PCNA variance are late G1 cells.