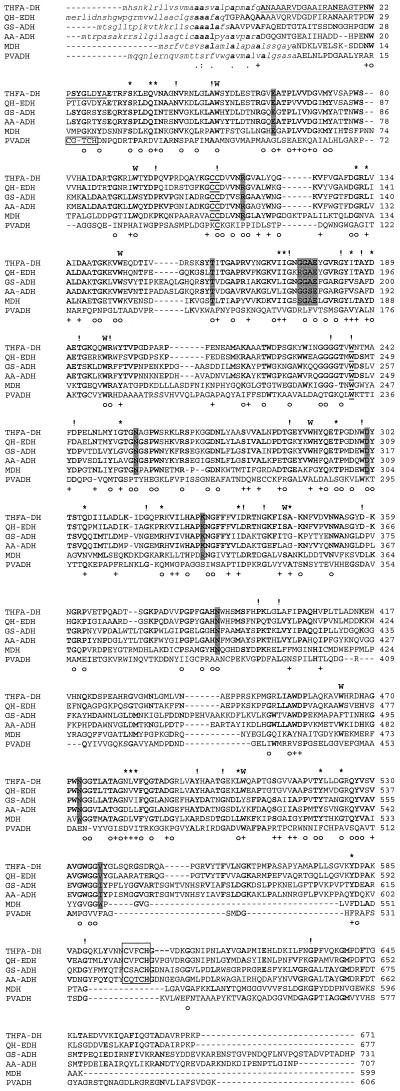
FIG. 3.
Multiple sequence alignment of TfaA from R. eutropha strain Bo (THFA-DH) with various quinoprotein ADHs: QH-EDH from C. testosteroni (Q46444); GS-ADH, quinoprotein ADH from Gluconobacter suboxydans (O05542); AA-ADH, quinoprotein ADH from A. aceti (P18278); MDH, methanol dehydrogenase from Methylobacterium extorquens (P16027); PVADH from Pseudomonas sp. P77931. Signal sequences are depicted in lowercase letters. Amino acids which were conserved in all investigated sequences are indicated on top of the alignment by !, similar residues are marked by ∗, and residues which are conserved in most sequences are indicated by boldface letters. Amino acids identical in all sequences, excluding PVADH, are indicated at the bottom of the alignment by ○, and similar residues are shown by +. The heme c binding sites are boxed, and amino acids supposed to be involved in PQQ binding are indicated by shaded boxes. The disulfide ring-forming cysteine residues and the opposite tryptophan residue are underlined. The tryptophan residues corresponding to tryptophan-docking motifs are indicated by a boldface W above the sequences. The N-terminal sequence previously determined by Edman degradation is underlined.