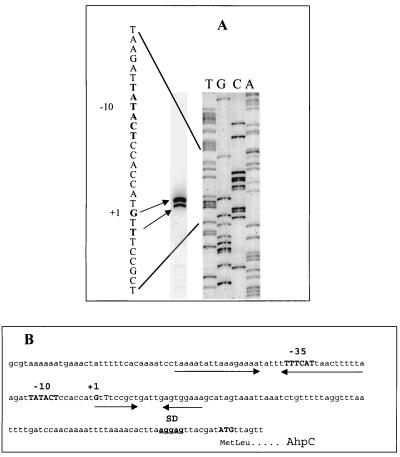
FIG. 8.
Primer extension analysis of ahpC. (A) To map the transcriptional start site of H. pylori AhpC mRNA, a [γ−32P]ATP-labeled oligonucleotide complementary to the 5′ end of ahpC was hybridized to 100 μg of total RNA and extended using reverse transcriptase. DNA sequencing reactions carried out with the same primer (right) were electrophoresed concomitantly with the primer extension products (left) to the left on a 6% urea polyacrylamide sequencing gel. Two potential 5′ ends of the ahpC transcript are 96 (G) and 94 (T) bp upstream from the AUG translation initiation codon. The potential −10 hexamer of the putative ahpC promoter is indicated in bold upstream of the transcriptional start site. (B) Shown is the DNA sequence of the region upstream of ahpC from H. pylori strain 26695. The potential ahpC transcription and translation start signals are shown in bold, as well as the Shine-Dalgarno (SD) ribosome binding site and the putative promoter sites centered at −10 and −35. The inverted repeats are indicated by arrows.