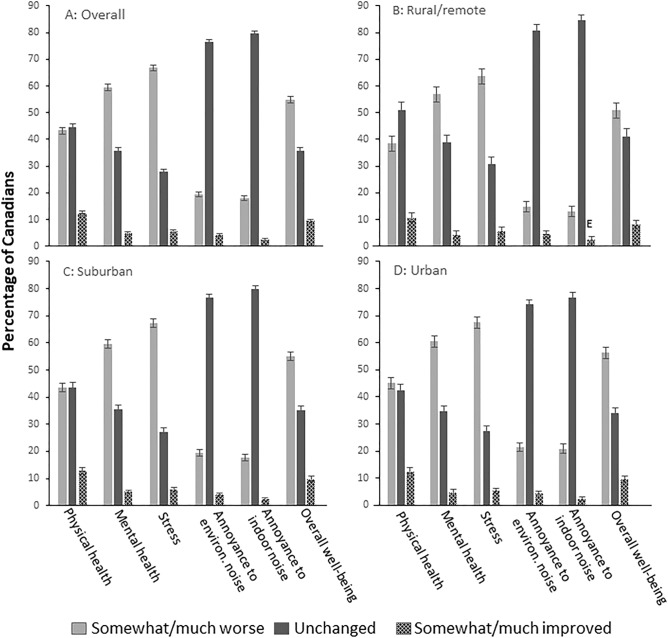
Figure 1.
Reported impact of COVID-19 on health-related outcomes and noise annoyance by geographic regions. (A) Overall, (B) Rural/remote regions, (C) Suburban regions, (D) Urban regions. Comparisons between geographic regions for each of the health-related outcomes and noise annoyance impacted by COVID-19 was carried out. Significantly higher (p < 0.05) prevalence of “somewhat/much worse” were observed in Suburban and Urban areas compared to Rural/remote areas in Physical health, Overall well-being, Annoyance toward environmental and indoor noise; Significantly lower (p < 0.05) prevalence of “unchanged” were observed in Suburban and Urban areas compared to Rural/remote areas in Physical health, Overall well-being, Annoyance toward environmental and indoor noise. Proportion of “somewhat/much improved” remained statistically similar across geographic regions in each outcome variable impacted by COVID-19.