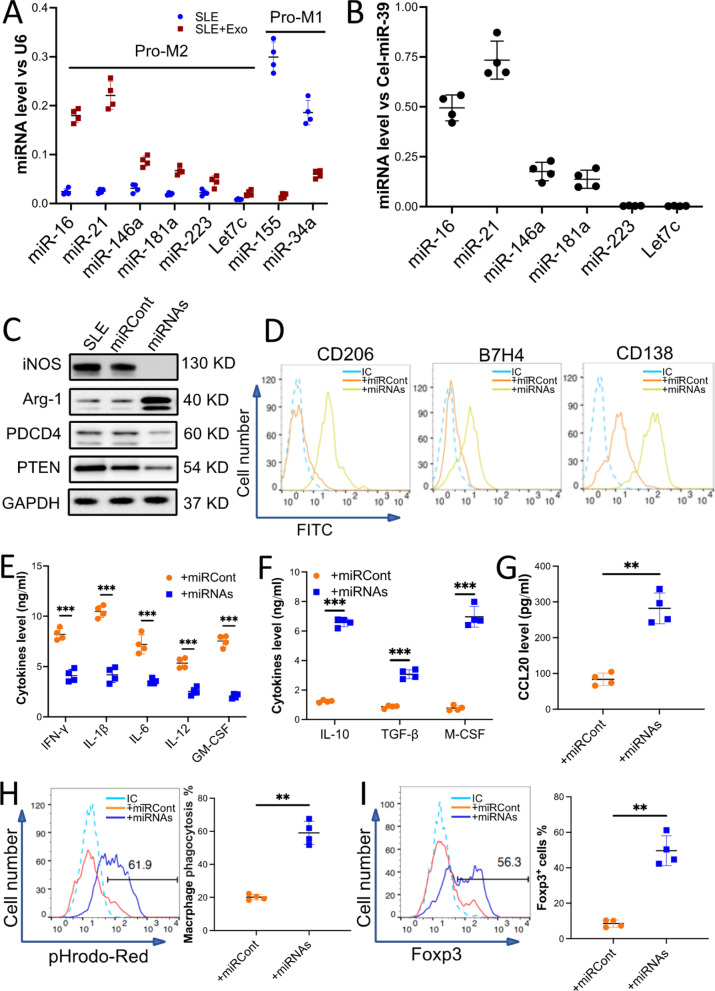
Fig. 4.
miR-16 and miR-21 enriched in the exosomes from BMMSCs contributed to the macrophage's unique anti-inflammatory polarization. Macrophages sorted from the kidneys of MRL/lpr mice (10 mice) were incubated with 50 µg/ml exosomes for 48 h (SLE + Exo), PBS treatment was used as a control (SLE). A The level of miRNAs that promote anti-inflammatory polarization (Pro-M2) or pro-inflammatory polarization (Pro-M1) in the macrophages with or without exosome treatment. B The relative level of miRNAs that promote macrophage anti-inflammatory polarization in the exosomes was calculated by qRT-PCR. Exogenous reference (Cel-miR-39) was added at exact amounts in each sample to estimate the efficiency of RNA extraction and reverse transcription (RT) reaction and to normalize the expression level of miRNAs in the exosome. C–H The macrophages were transduced with miRNA-Lentivirus to overexpress miR-16 and miR-21 (+ miRNAs). The miRNA-Lentivirus control was used as a control (+ miRCont). The levels of iNOS, Arg-1, PTEN, and PDCD4 in the miRNAs’ overexpressed macrophages were examined by immunoblotting analysis. GAPDH was used as a control (C). Macrophage surface markers CD206, B7H4, and CD138 (D) were checked by using flow cytometry. Macrophage-secreted pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines (E and F) or chemokine CCL20 (G) was detected by ELISA. The efferocytosis of pHrodo Red-labeled apoptotic TCMK-1 cells by the macrophages (H). I Naïve T cells were incubated with CdM of macrophages that overexpressed miRNAs. The percentage of Fox3p+ iTreg was checked by flow cytometry. Data are expressed as mean ± SD of n = 4, unless specified. **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001. IC, isotype control