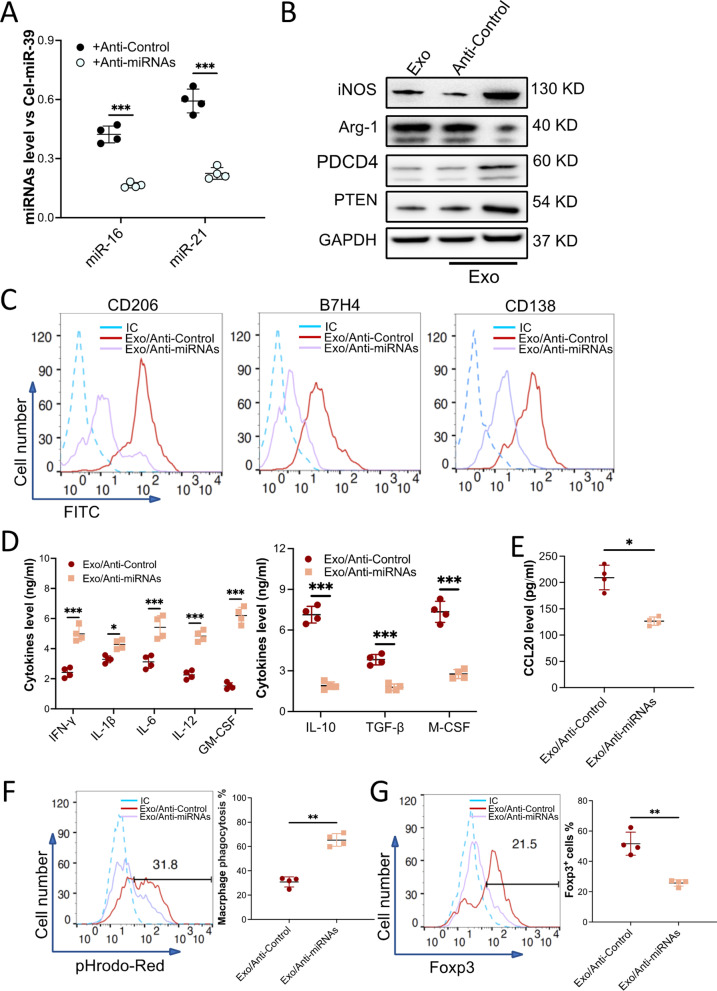
Fig. 5.
Exosome-induced macrophage polarization was attenuated when miR-16 and miR-21 were depleted in the exosomes. BMMSCs were transduced with Lentivirus/anti-miR-Control (+ Anti-Control) or with Lentivirus/anti-miR-16 and anti-miR-21 (+ Anti-miRNAs) to knock down miR-16 and miR-21. Exosomes from these cells were collected. A The level of miR-16 and miR-21 in the exosomes was validated with qRT-PCR. Cel-miR-39 was introduced as an exogenous reference for the normalization of miRNAs in the exosome. B–F Macrophages sorted from the kidney of MRL/lpr mice were treated with miR-16 and miR21-downregulated exosomes (Exo/Anti-miRNAs, n = 4). Exosome collected from BMMSCs that received Lentivirus/anti-miR-Control (Exo/Anti-miR-Control, n = 4) was used as a control. The levels of iNOS, Arg-1, PTEN, and PDCD4 in the macrophages were examined by immunoblotting analysis. GAPDH was used as controls (B, n = 3). Macrophage surface markers CD206, B7H4, and CD138 (C) were checked by using flow cytometry. Macrophage-secreted pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines (D) or chemokine CCL20 (E) were detected by ELISA. The efferocytosis of pHrodo Red-labeled apoptotic TCMK-1 cells by the macrophages (F). G Naïve T cells were incubated with CdM of macrophages that were treated with the exosomes. The percentage of Fox3p+ iTreg was checked by flow cytometry. Data are expressed as mean ± SD of n = 4, unless specified. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001. IC, isotype control