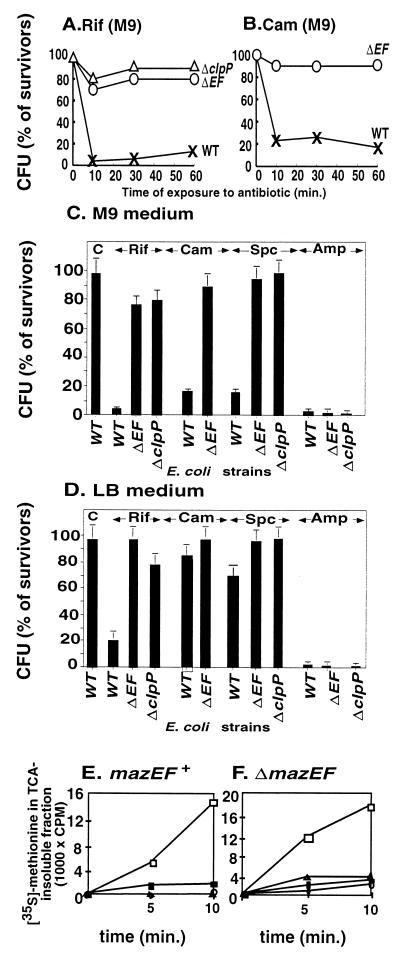
FIG. 1.
Antibiotics that inhibit transcription and/or translation in E. coli induce mazEF-dependent cell death. Viability plotted against the time of exposure to rifampin (A) and chloramphenicol (B) in M9 medium of E. coli MC4100 relA+ (WT) (x) and its ΔmazEF (ΔEF) (O) and ΔclpP (Δ) derivatives is shown. (C) The viability of E. coli MC4100 relA+ (WT) and its ΔmazEF (ΔEF) and ΔclpP derivatives in M9 medium either untreated (C, control) or treated for 10 min with rifampin (Rif), chloramphenicol (Cam), spectinomycin (Spc), or ampicillin (Amp). (D) As for panel C but in LB medium. (E) The effects in M9 medium of the antibiotics (untreated cells, □; rifampin, ■; chloram phenicol, ●; spectinomycin, ▴) on protein synthesis in E. coli MC4100 relA+. (F) As for panel E but in the derivative strain MC4100 relA+ ΔmazEF. The effects of the antibiotics on mazEF-mediated killing and on protein synthesis were measured as described in Materials and Methods.