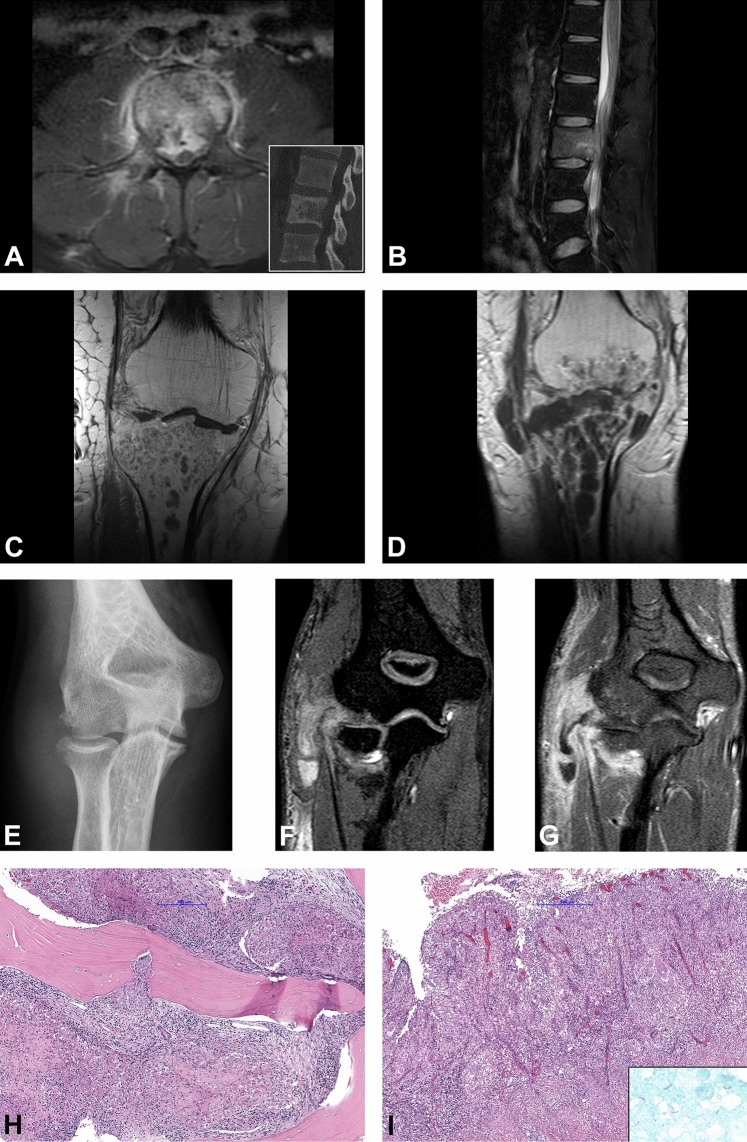
Fig. 3.
Radiological and histological findings. a, b 31-year-old male patient with a diffuse pathological contrast enhancement of the L2 and paravertebral soft tissue component on axial T2w fat-saturated MRI image (a). Osteolytic destruction of the vertebral body on sagittal CT image (inset). Sagittal T2w fat-saturated image shows bone marrow edema of the vertebral body with epidural abscess and spinal cord compression (b). Timely evolution of the intraosseous abscess formations in the proximal tibia in the 69-year-old-male patient on coronal post contrast T1w sequences baseline MRI (c) and after 1 month (d). Radiological signs of pyogenic arthritis with the osteo destruction of the tibial plateau and newly developed involvement of the distal femur and para-articular soft tissues medially. Antero-posterior plain radiograph of the right elbow in a 20-year-old female patient shows osteo destruction of the humeral capitellum with soft tissue edema (e). 3-dimensional T1w WATS (Water Selective Excitation) coronal image (f) shows a widening of the radio-humeral joint with osteo destruction of the periarticular bones, synovial proliferation, and pathological contrast enhancement of the periarticular soft tissue with abscess formation along the flexor muscles of the forearm (g). Granulomatous inflammation composed of granulomas with central necrotic areas surrounded by the palisading histiocytes involving the bone (h) and the soft tissue (i). Ziehl–Neelsen staining shows scattered acid-fast organisms (i inset)