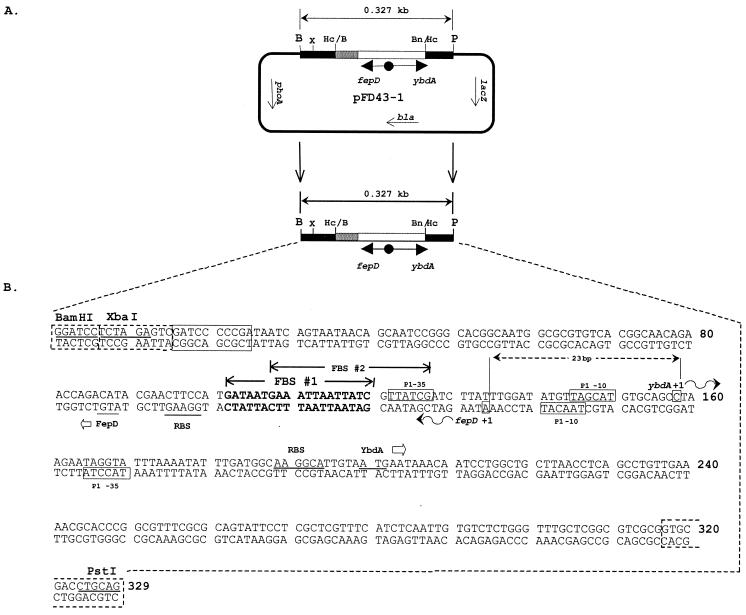
FIG. 1.
The fepD-ybdA bidirectional transcription fusion vector and sequence of the transcriptional control region. (A) Structure of the wild-type promoter construct, pFD43-1, with fepD fused to phoA and ybdA to lacZ. Abbreviations for the restriction enzymes used: B, BamHI; Bn/Hc, BanI-HincII hybrid site; Hc/B, HincII-BamHI hybrid site; P, PstI; X, XbaI. Plasmid reporter genes are lacZ (β-galactosidase) and phoA (alkaline phosphatase); bla is the selectable β-lactamase gene and serves as an internal standard for transcript quantitation. Arrows within constructs designate the direction of the transcripts. (B) Sequence of the 329-bp region containing the promoter cassette used for mutagenesis, nucleotide sequencing, and reporter gene analysis. The BamHI and PstI cloning sites are noted. Boxed sequences at the termini originate from the vectors used in construction steps (see Materials and Methods). The boxes with dashed edges are from the M13mp19 polylinker, and the solid box near the left end of the sequence is from the pCON4 vector. These sequences are represented by the black and gray boxes, respectively, in the vector map in panel A (not to scale). Predicted overlapping primary 19-bp Fur-binding core sequences are identified and labeled FBS #1 and FBS #2. Putative primary promoter elements (P1) for the fepD and ybdA genes are represented and labeled. The +1 primary transcriptional start sites for ybdA and fepD are identified, and the curved arrows denote the direction of transcription. The proposed ATG translational start sites for both the FepD and YbdA proteins and their predicted corresponding ribosome binding sequences are underlined. Nucleotides are numbered 5′ to 3′ from the BamHI site to the PstI site.