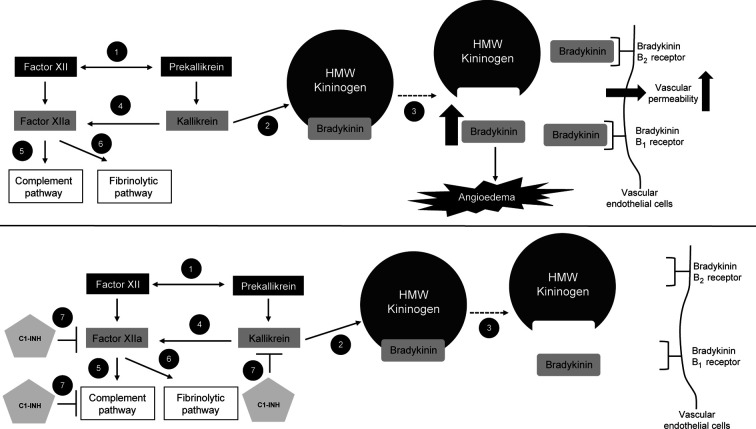
Figure 1.
Dysregulation of signaling pathways in HAE. (1) When activated by trace amounts of factor XIIa, plasma prekallikrein and factor XII cleave each other to generate kallikrein and factor XIIa. (2) Kallikrein cleaves HMW plasma kininogen, leading to (3) the release of bradykinin. (4) Plasma kallikrein cleaves factor XIIa, leading to (5) activation of complement and (6) fibrinolytic pathways. In the top figure, the increase in bradykinin levels results in angioedema. Bradykinin binds bradykinin B1 and B2 receptors on vascular endothelial cells, leading to an increase in vascular permeability. In the bottom figure, (7) C1-INH inhibits factor XIIa, the complement pathway, and kallikrein, thus leading to a decrease in bradykinin production and reduced activation of bradykinin B1 and B2 receptors on vascular endothelial cells. C1-INH, C1 esterase inhibitor; HAE, hereditary angioedema; HMW, high molecular weight. Figure created with data from Cicardi M, et al. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. (2018) 6(4):1132–41; and Zuraw BL. N Engl J Med. (2008) 359(10):1027–36 (5, 16).