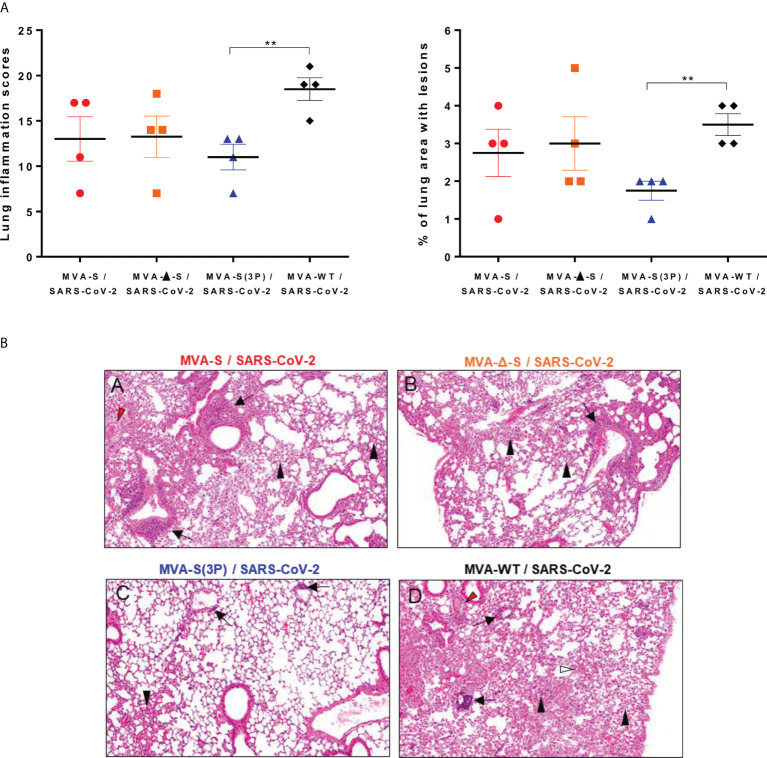
Figure 4.
One IN dose of MVA-S(3P) reduced SARS-CoV-2 lung pathology in K18-hACE2 transgenic mice. (A) Lung inflammation scores (left) and percentage of lung area with lesions (right) examined in lung samples taken from mice (n = 4/group) vaccinated and infected as indicated in Figure 3A , and euthanized at 5 days postchallenge. Mean and SEM of cumulative histopathological lesion scores (left) and percentage of lung area affected by inflammatory lesions (right). Unpaired t-test: **p < 0.01. (B) Representative lung histopathological sections (H&E staining) from K18-hACE2 mice euthanized at day 5 postchallenge (magnification: 10×). Mice immunized with one dose of MVA-S (A) and MVA-Δ-S (B) displayed moderate inflammatory lung lesions that were, in general, more severe and extensive in mice immunized with MVA-WT (control infected group; d). These lesions highlighted the presence of diffuse thickening of the alveolar septae, perivascular edema (red arrowheads), mononuclear cell infiltrates within alveolar spaces (black arrowheads), large multifocal perivascular and peribronchiolar mononuclear infiltrates (black arrows), and occasional hemorrhages (white arrowheads). However, mice immunized with MVA-S(3P) (C) only displayed small lung areas with mild inflammatory lesions such as focal thickening of alveolar septae, occasional presence of mononuclear cell infiltrates within alveolar spaces (black arrowheads), and mild perivascular or peribronchiolar mononuclear infiltrates (black arrows).