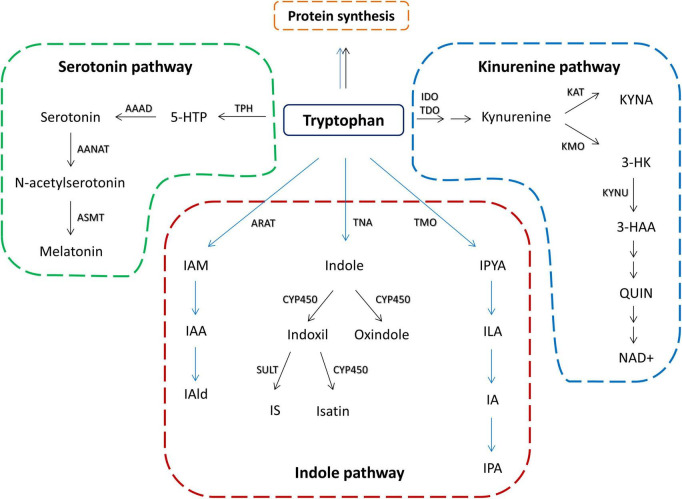
FIGURE 1.
Schematic overview of tryptophan metabolic pathways in the host and its commensal bacteria. Black arrows represent host metabolism. Blue arrows represent microbial metabolism. Serotonin pathway – TPH, tryptophan hydroxylase; 5-HTP, 5-hydroxytryptophan; AAAD, aromatic amino acid decarboxylase; AANAT, aralkylamine N-acetyltransferase; ASMT, acetylserotonin O-methyltransferase; kynurenine pathway – IDO, indolamine 2,3-dioxygenase; TDO, tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase; KAT, kynurenine aminotransferase; KYNA, kynurenine acid; KMO, kynurenine 3-monooxygenase; KYNU, kynureninase; 3-HK, 3-Hyroxykynurenine; 3-HAA, 3-hydroxyanthranilic acid; QUIN, quinolinic acid; NAD+, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide; indole pathway: ARAT, aromatic amino acid aminotransferase; IAM, indole-3-acetamide; IAA, indole acetic acid; IAld, indole-3-aldehyde; TNA, tryptophanase; CYP450, cytochrom P450 enzymes; SULT, sulfotransferase; IS, indoxil-3-sulfate; TMO, tryptophan 2-monooxygenase; IPYA, indole-3-pyruvate; ILA, indole-3-lactic acid; IA, indole acrylic acid; IPA, indole-3-propionic acid.