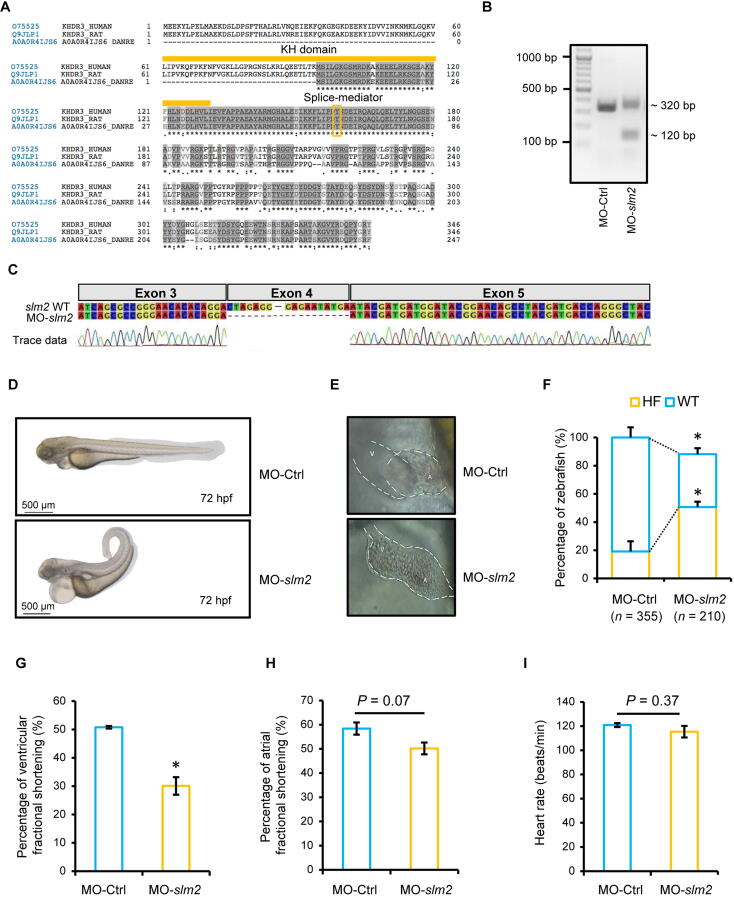
Figure 2.
slm2 knockdown results in heart failure in zebrafish
A. Conservation of the SLM2 proteins in humans, rats, and zebrafish. The KH domain which mediates RNA interaction and the tyrosine (Y) residue which mediates splicing are labeled. B. PCR analysis of zebrafish injected with splice morpholino targeting slm2 mRNA (MO-slm2) or control MO (MO-Ctrl) at 1–2-cell-stage embryos. The 320-bp product indicates the wild-type slm2 and the 120-bp product indicates loss of function by exon skipping. C. The effectiveness of MO-slm2 validated by Sanger sequencing of the PCR products shown in (B). D. Representative images of zebrafish injected with MO-slm2 and MO-Ctrl, respectively. Scale bar, 500 µm. E. Magnification of the hearts of zebrafish shown in (D). F. Quantitative analysis of the phenotypes of zebrafish after MO-slm2 or MO-Ctrl injection. G. Ventricular fractional shortening of zebrafish after MO-slm2 or MO-Ctrl injection. H. Atrial fractional shortening of zebrafish after MO-slm2 or MO-Ctrl injection. I. Heart rate of zebrafish after MO-slm2 or MO-Ctrl injection. *, P < 0.05 (Student’s t-test). A, atrium; V, ventricle; HF, heart failure; WT, wild-type.