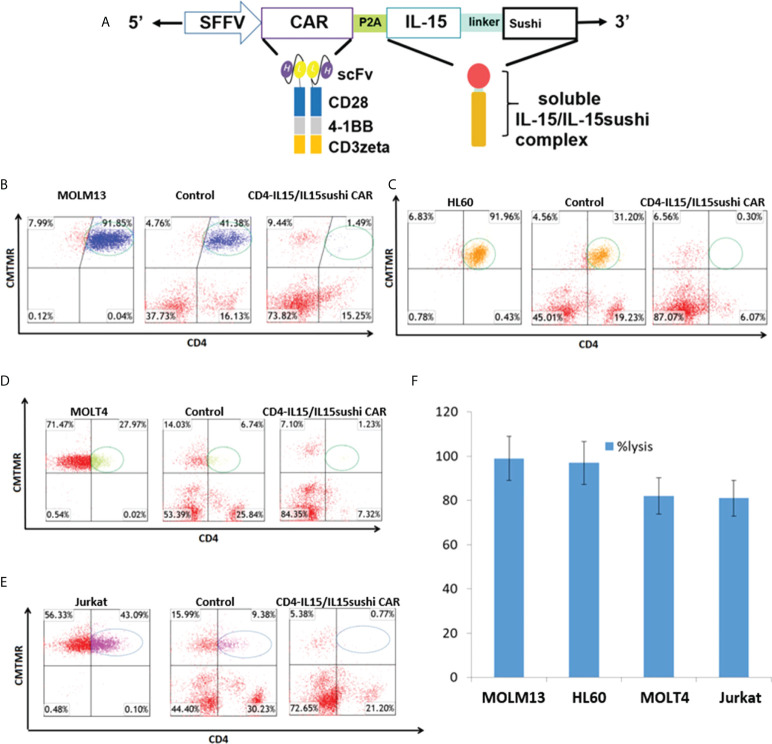
Figure 1.
CD4-IL15/IL15sushi construct and in vitro validation. (A) Schematic representation of recombinant lentiviral vector encoding a third generation CD4 CAR linked with the P2A self-cleaving sequence to the IL-15/IL-15sushi domain of the IL-15 alpha receptor. Expression is driven by the spleen focus-forming virus (SFFV) promoter. The IL-15/IL-15sushi portion is composed of an IL-2 signal peptide fused to IL-15 and linked to the sushi domain via a 26-amino acid poly-proline linker. (B) Target MOLM13 cells expressing CD4 were co-cultured with control T cells (middle panel) or CD4-IL15/IL15sushi CAR T cells (right panel) at an E:T ratio of 2:1 for 24 hours. Left panel shows target cells alone. Target cells were pre-stained with CellTracker (CMTMR) to help distinguish from CD4-IL15/IL15sushsi CAR T cells. T cells are displayed in red. 97% of circled target population lysed compared to control in average of two experiments. (C) Target HL60 cells used in same experimental design. 99% of circled target population lysed compared to control in average of two experiments. (D) Target MOLT4 cells used in same experimental design. 82% of circled target population lysed compared to control in average of two experiments. (E) Target Jurkat cells used in same experimental design. 82% of circled target population lysed compared to control in average of two experiments. (F) Percent lysis of target population by CD4-IL15/IL15sushi CAR T cells compared to control T cells from (B–E). Each bar represents the average of duplicate samples.