Figure 3.
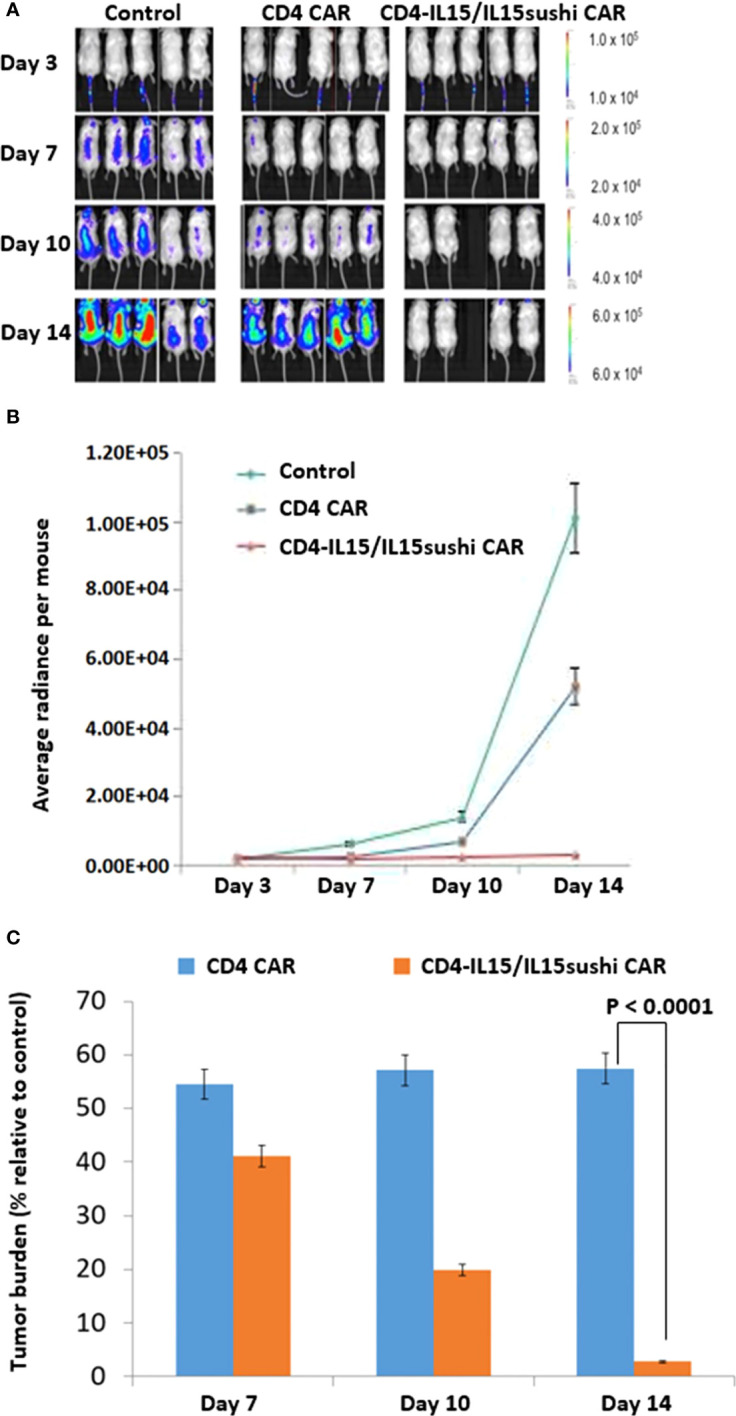
CD4-IL15/IL15sushi CAR NK92 cells reduce tumor burden in Jurkat mouse model. (A) NSG mice were sub-lethally irradiated and intravenously injected with 1.0x106 luciferase-expressing Jurkat cells to induce measurable tumor formation. Three days following tumor cell injection, 5 mice were intravenously injected with a course of 10x106 vector control NK92, CD4 CAR NK92, or CD4-IL15/IL15sushi CAR NK92 cells. On days 3, 7, 10, and 14, mice were injected subcutaneously with RediJect D-luciferin and subjected to IVIS imaging to measure tumor burden. One mouse died on Day 10 after NK92 injection, most likely due to injection procedure and NK92 cell aggregation. This mouse was sick immediately after injection. (B) Average light intensity for control NK92, CD4 CAR NK92, and CD4-IL15/IL15sushi CAR NK92 cells was measured in average total flux (photons/sec). CD4-IL15/IL15sushi CAR NK92 cells had lower light intensity than control and CD4 CAR groups. (C) Average light intensity measured for CD4 CAR and CD4-IL15/IL15sushi CAR was compared to that of control to determine the tumor burden in treated versus control mice. Although both conditions showed significant reduction in tumor burden by Day 7, relative tumor burden for CD4 CAR NK92 cells stayed the same to Day 14, while CD4-IL15/IL15sushi CAR NK92 cells continued to decrease by over 97%. Unpaired t-test analysis revealed an extremely significant difference (P < 0.0001) between the CD4 CAR NK92 and CD4-IL15/IL15sushi CAR NK92 treatment groups by Day 14.
