Figure 1.
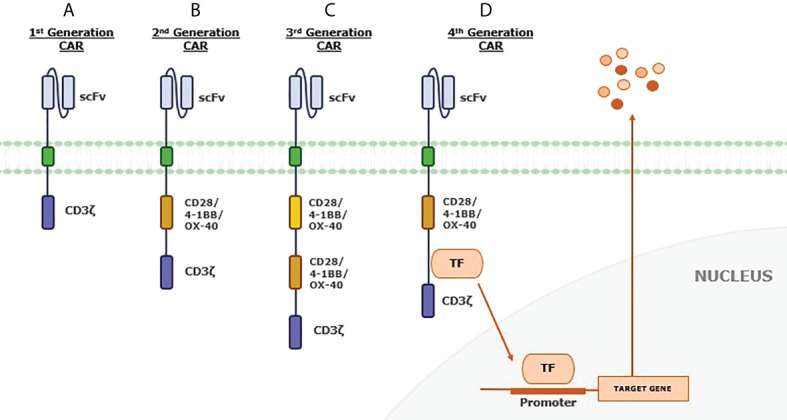
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) generations. (A) First-generation CAR includes a single-chain variable fragment (scFv) extracellular region and a T-cell activation domain. This minimal structure can recognize the antigen in an HLA-independent manner. By adding a costimulatory domain, (B) second-generation CAR is more able to expand and persist due to this second signal. (C) The third-generation CAR has an additional costimulatory signaling domain to increase proliferation, survival, and activity of engrafted T cells. Recently, (D) the fourth-generation CAR has been developed to include extra genes, such as recognition domains for transcription factors involved in mediating signal transduction. The idea is to modulate the effect of the CAR, facing an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment by cytokine production or other additional effects.
