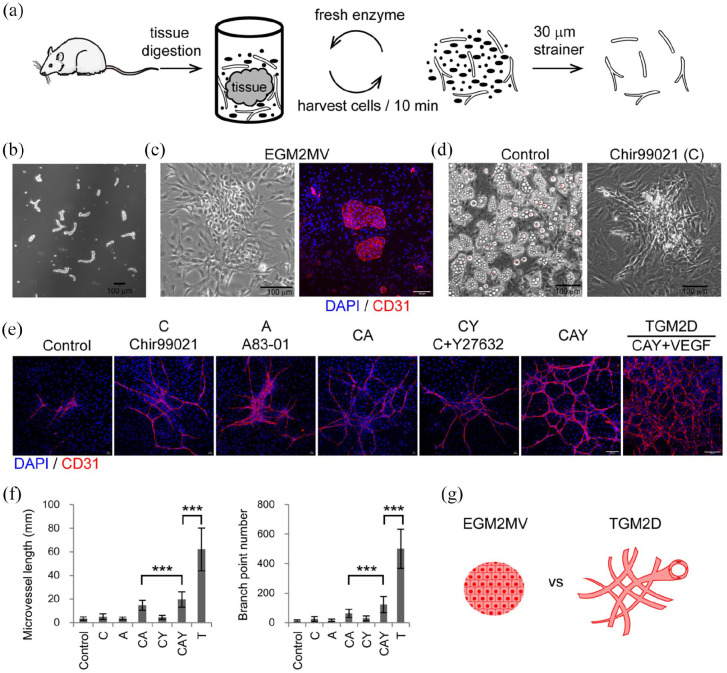
Figure 1.
Expand adult tubular microvessels in vitro: (a) the procedure of isolating microvessels from adult SD rats’ subcutaneous soft connective tissues by cyclic enzymatic digestion, (b) phase contrast image of primary microvessels, (c) phase contrast and immunofluorescence images of the microvessels cultured in EGM2MV medium, (d) phase-contrast images of the primary microvessels cultured in the media of control and Chir99021, (e) immunofluorescence images of primary microvessels cultured in different media,(f) quantification of the microvessels in different experimental groups including control (n = 81), C (n = 84), A (n = 72), CA (n = 97), CY (n = 58), CAY (n = 61), and TGM2D (CAY + VEGF) (n = 9). Data were presented as mean ± SD. One-way ANOVA was performed on the data, followed by Bonferroni post hoc tests. ***p < 0.001, and (g) illustration of the morphologies of microvessels cultured in EGM2MV and TGM2D. The antibody against CD31 was used to label endothelial cells. DAPI was used to label cell nuclei. Scale bars, 100 μm.